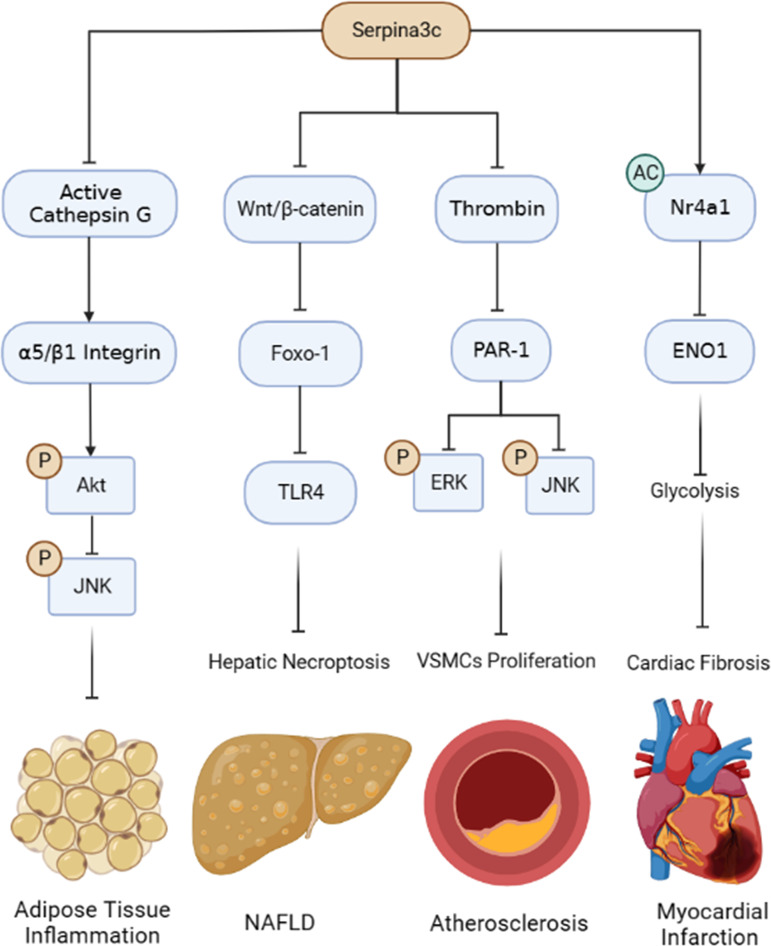
Figure 7.
Summary of the protective roles and mechanisms of Serpina3c in pathophysiological processes. Serpina3c inhibits adipose tissue inflammation by inhibiting Cathepsin G, maintaining integrin α5/β1 integrity, activating AKT and inhibiting JNK phosphorylation. Serpina3c can inhibit non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin signal pathway in hepatocyte, reducing the transcription of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) by Foxo-1, and inhibiting hepatic necroptosis. Seprina3c can bind and inhibit thrombin activity, prevent its cleavage and activation of protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1), weaken its downstream ERK and JNK phosphorylation, and inhibit the excessive proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), thus inhibiting atherosclerosis. Serpina3c can bind to nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 1 (Nr4a1) in the mice cardiac fibroblasts nuclei and promote its acetylation, inhibits the transcription of enolase 1 (ENO1) and suppresses the excessive activation of glycolysis, thus alleviating cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction. (Created with BioRender.com).