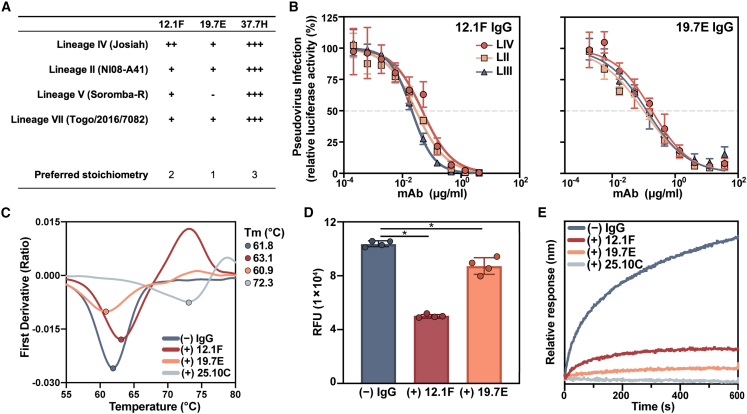
Figure 3.
Characterization of the neutralizing GP1-A-specific mAbs 12.1F and 19.7E
(A) Summary of mAb binding to GPCs by BLI (raw data in Figure S7). Binding efficiency is based on the relative on-rate of IgG to immobilized GPCs and is indicated as follows: +++, very strong binding; ++ strong binding; +, moderate binding; −, minimal binding. Proposed IgG stoichiometry per GPC is estimated based on relative Rmax values under the assumption that the highest Rmax indicates full occupancy and that 37.7H has a preferred occupancy of 3 Fabs per trimer, as in the crystal structure.30
(B) mAb neutralization of pseudoviruses derived from LASV LIV (strain Josiah), LII (strain NIG08-A41), and LIII (strain CSF). Dotted lines indicate 50% neutralization. Data points represent the mean with error bars indicating the SEM of three technical replicates.
(C) Thermostability of LIV GPC-I53-50A in complex with indicated Fabs assessed by nanoDSF. Points represent the Tm of each complex. Each melting curve is a representative of triplicate curves with Tm within ±0.1°C.
(D) Synthetic matriglycan competition microarray measuring StrepTagged GPC-I53-50A binding to matriglycan with and without pretreatment with 12.1F and 19.7E IgG. GPC-I53-50A bound to matriglycan was detected using StrepMAB Ab (Figure S9E). Column height reflects the mean RFU with error bars indicating standard deviation. Statistical differences between the groups (n = 4 technical replicates) were determined using two-tailed Mann-Whitney U tests (∗p < 0.05).
(E) BLI competition analysis of immobilized GPC bound to indicated IgG and then exposed to recombinant LAMP-1 at a pH of 5 (Figure S9F). Presented data indicate representative curves from three technical replicates.