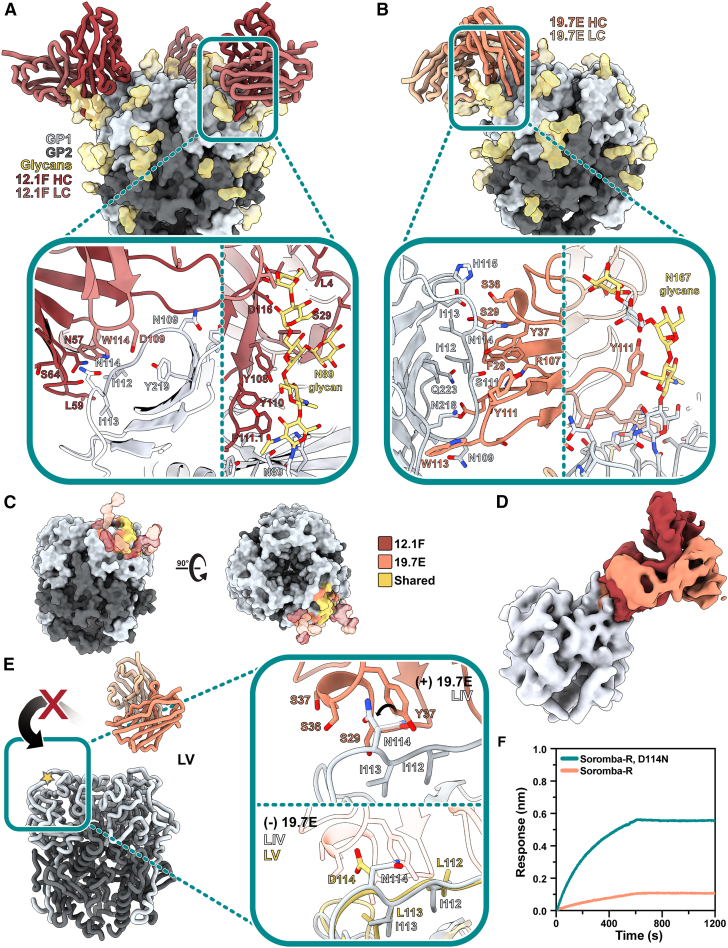
Figure 4.
Structural description of the GP1-A epitope cluster
(A) Atomic model of LIV GPC (gray) bound to 12.1F Fab (red) determined by cryo-EM. Inset depicts key interactions between GP1 and 12.1F Fab at the epitope-paratope interface. Glycans within close proximity (<4 Å) shown in gold. More details can be found in Table S2.
(B) Atomic model of LIV GPC (gray) bound to 19.7E Fab (orange) determined by cryo-EM. Inset depicts key interactions between GP1 and 19.7E Fab at the epitope-paratope interface. Glycans within close proximity (<4 Å) shown in gold. More details can be found in Table S3.
(C) The GP1-A antigenic landscape mapped on LIV GPC and colored according to the 12.1F (red), 19.7E (orange), or shared (yellow) Ab footprint. Glycan contacts are noted as transparent surfaces colored according to Fab interaction.
(D) Overlaid, Gaussian-filtered maps showing the angle of approach taken by 12.1F (red) and 19.7E (orange) Fabs to engage LIV GPC (gray).
(E) Analysis of the residues at the 19.7E binding site for LIV and LV GPCs. The gold star indicates the loop in the inset panels (right). The top panel shows the LIV GPC conformation when bound to 19.7E with the rotameric shift of LIV’s N114 shown. The bottom panels shows both LIV and LV GPCs in their unliganded conformation with 19.7E shown in translucent orange to indicate its positioning when bound to the LIV GPC. Marked residues indicate differences in the amino acid sequences of LIV and LV.
(F) BLI binding analysis of immobilized 19.7E IgG binding to 140 nM of the following LV GPC-I53-50As: native strain Soromba-R (orange) or Soromba-R featuring a D114N mutation (teal; left). Presented data indicate representative curves from three technical replicates.