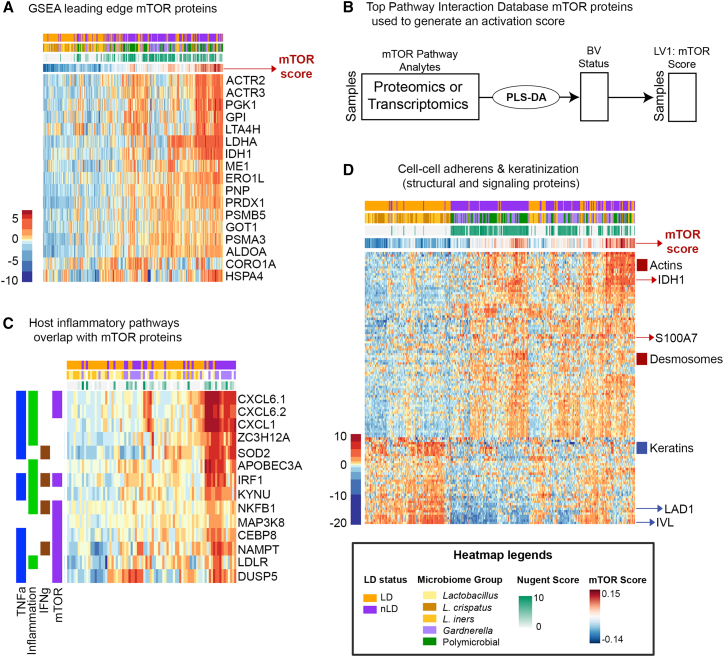
Figure 3.
Relationship between the mTOR activity signature in the vaginal microenvironment
(A) Heatmap of the leading mTOR edge proteins identified by GSEA and relationship to vaginal microbiome.
(B) Core mTOR proteins identified using the Pathway Interaction Database were used to identify mTOR expression. An mTOR activity score was determined using partial least-squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) inference of the latent variable combining pathway proteins or transcripts to describe mTOR pathway activity relative to LD status (“mTOR Score”). This numeric score was then used to determine both host and bacterial factors that associate with a high mTOR score. See Figure S2A for mTOR score analysis performed using Nugent score.
(C) Vaginal tissue gene expression for immune response pathways (inflammation, TNFα, IFNγ) overlapped with genes associated with mTOR and LPS-stimulated genes identified using significant pathways identified GSEA when comparing Lactobacillus-dominant (LD) with non-dominant (nLD) groups.
(D) mTOR score is significantly correlated with measured epithelial barrier protein expression in the mucosal fluid (Spearman’s correlations, p < 0.0001) showing key distinctions in barrier function and structural changes that were clearly separated by cluster analysis.