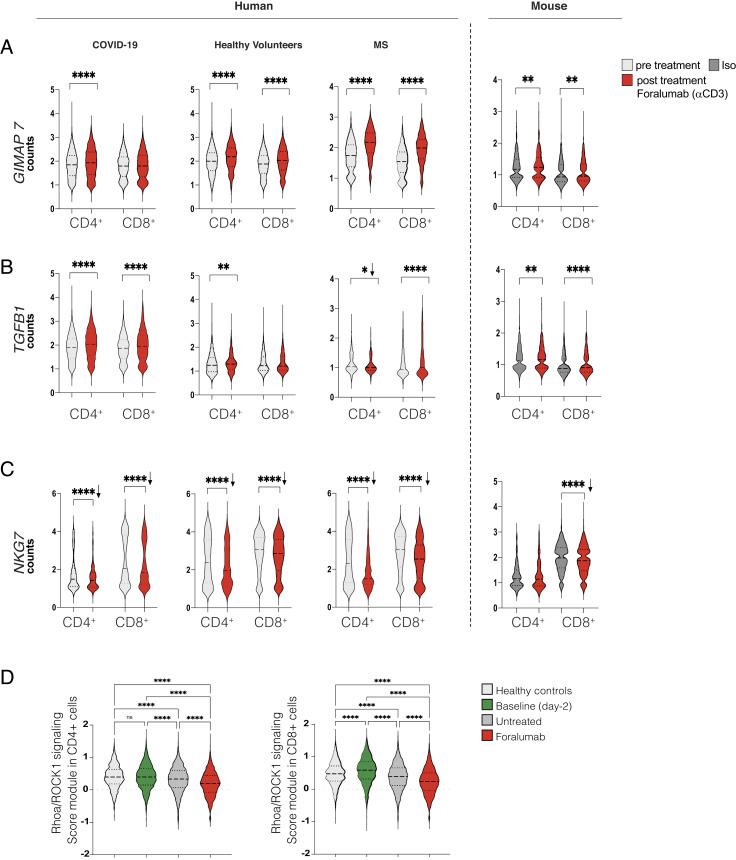
Fig. 2.
GIMAP7, TGFB1, and NKG7 Gene Expression Changes Play a Key Role in Foralumab Modulatory Effects. (A–C) Foralumab-modulated gene expression of GIMAP7 (A) TGFB1 (B) and NKG7 (C) counts across cell types and treatment. COVID-19 subjects were treated intranasally with 100 µg of Foralumab for 10 consecutive days. Analysis shows before treatment (day -2) and after Foralumab (day 10). Data from healthy volunteers were obtained in a dose escalation study. Selected data reflect a dose of 50 µg given for 5 d (n = 6). Subjects were followed up for 30 d. MS subject is a 61-y-old male with non-active progressive MS treated with 50 µg of Foralumab three times a week for two consecutive weeks (one cycle) followed by 1 wk interval. A total of five cycles was completed. Analysis shows before treatment vs. after treatment. C57BL/6 mice were treated intranasally with 1 µg of anti-CD3 (clone 145-2C11, Novus Biologicals) or isotype control (Iso) for five consecutive days. CD3+ cells from cervical lymph node were FACS-sorted. For human studies, CD3+ cells were obtained from PBMC. Violin plots are median ± IQR. Student’s t test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.001. Arrows shows downregulation. (D) Gene expression levels of RhoAROCK1and CFL1 values was aggregated (RhoA/ROCK1 pathway) and scored in CD4+ and CD8+ cells of healthy controls, Baseline (day -2) and untreated and Forlaumab subjects on day 10. One-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc was used for analysis. ****P < 0.001