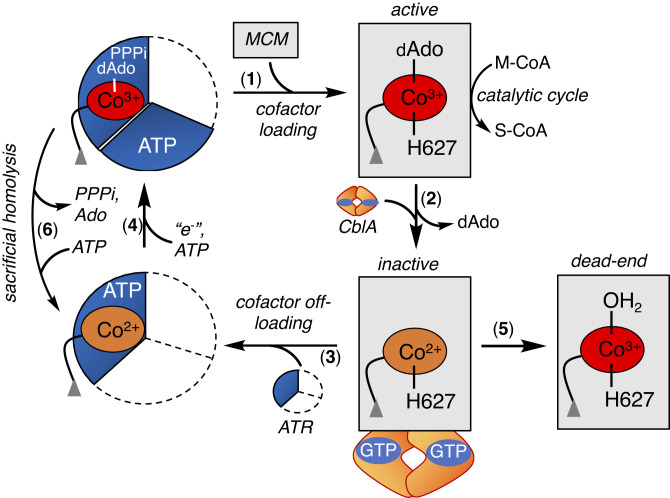
Fig. 1.
Mitochondrial chaperones support MCM function. Once loaded with AdoCbl from ATR (1), MCM catalyzes multiple rounds of isomerization of M-CoA to succinyl-CoA (S-CoA) (2). The occasional loss of dAdo from the active site leads to inactive cob(II)alamin (3), which in the presence of CblA and GTP is off-loaded onto ATR for repair (4). Formation of H2OCbl on MCM precludes cofactor off-loading (5). If the newly formed AdoCbl is not transferred to MCM, ATR catalyzes a sacrificial cobalt–carbon bond homolysis (6). ATR is a homotrimer and the occupied active sites are shown in blue.