Figure 1.
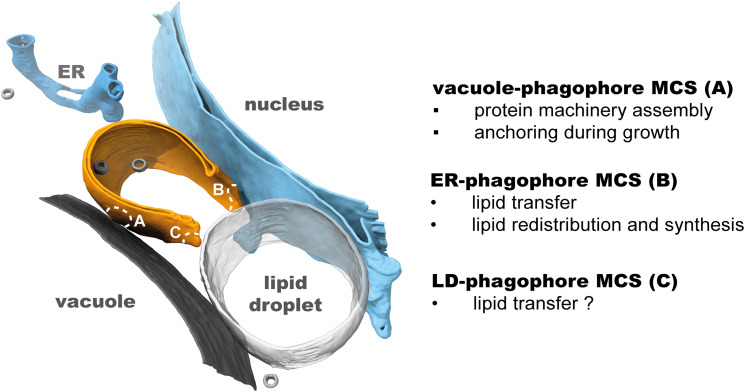
Membrane contact sites (MCSs) contribute to phagophore formation and growth. The double membrane phagophore (orange) establishes multiple contact sites during growth. It is anchored to the vacuole at its side or back (A), whereas its rim establishes contact with the ER, including tubular ER (see Figure 3) and the nuclear membrane (B). In addition, it can also directly interact with lipid droplets (C). In this example, all three interorganelle MCSs are captured in situ in S. cerevisiae by correlative cryo-ET and can be appreciated in the 3D rendering of the segmented membranes (Bieber et al., 2022; EMD-15548).