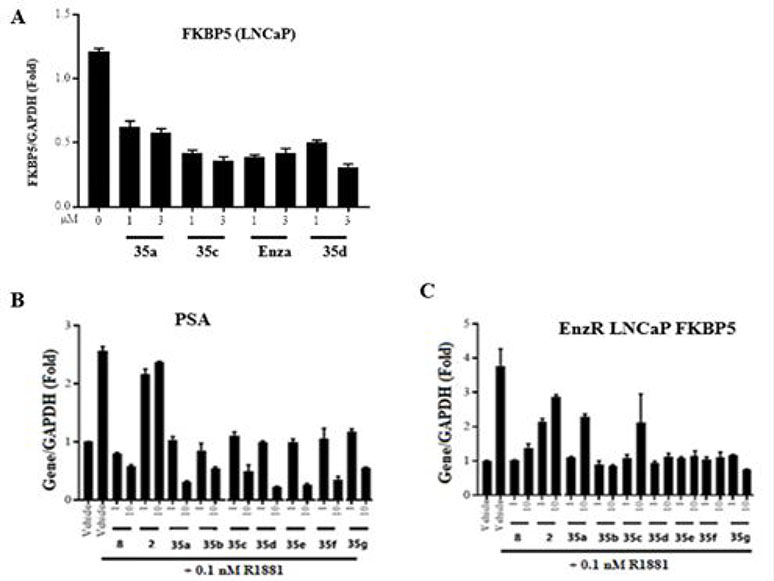
Figure 6.
Effect of 35-series compounds on transcription of AR-regulated gene FKBP5 and PSA in prostate cancer LNCaP cells, and FKBP5 in enzalutamide-resistant LNCaP cells. (A-B) LNCaP cells or (C) enzalutamide-resistant LNCaP cells were plated and maintained in RPMI+1%FBS medium for 2 days prior to treatment with AR agonist R1881 (0.1 nM) and the drug indicated in the figure as antagonist (1, 3, or 10 μM). After 24h, total RNA was isolated, analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) with the indicated primers and probes. Signals were normalized to those of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Detection of mRNA encoding (A) AR target gene FKBP5, (B) prostate-specific antigen (PSA), or (C) FKBP5 in enzalutamide-resistant LNCaP cells. Levels of each mRNA were compared to those after treatment with enzalutamide (compound 2) or (B–C) enzalutamide (compound 2) and UT-155 (compound 8). These compounds antagonized the function of AR in both LNCaP cells and LNCaP cell derivatives that are enzalutamide resistant.