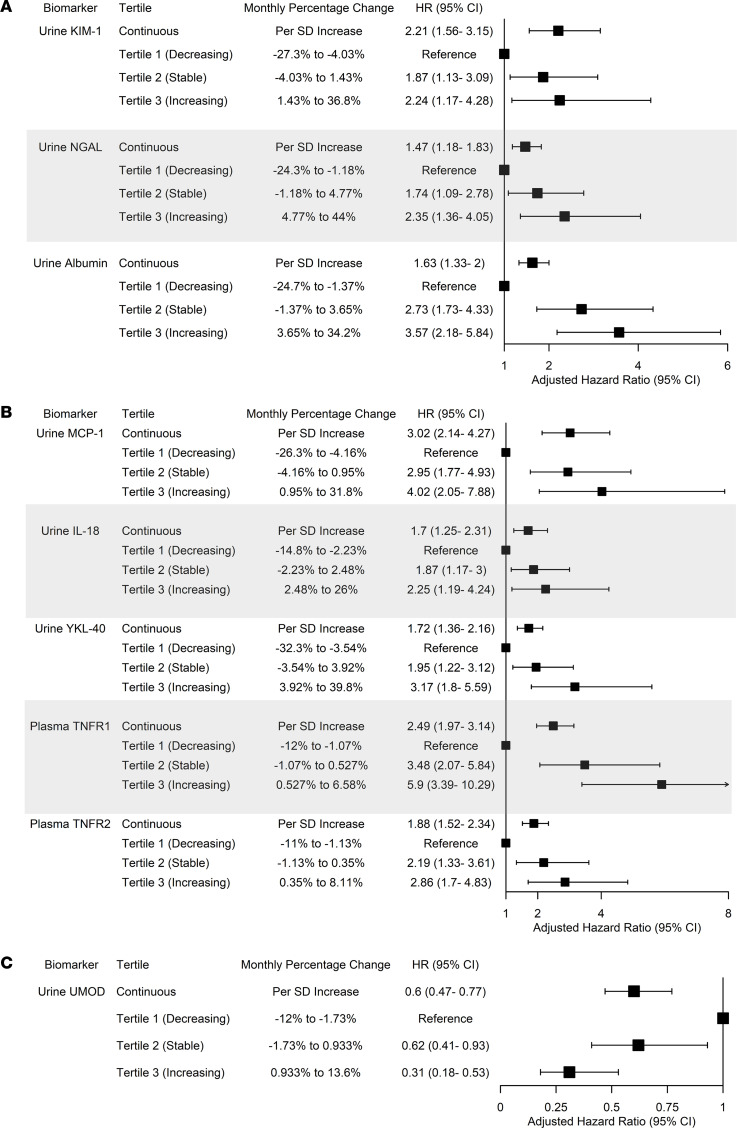
Figure 2. Associations between slopes of biomarkers of kidney injury, inflammation, and tubular health with the composite outcome of incident CKD and CKD progression.
(A–C) Association between biomarkers of kidney injury (A), inflammation (B), and tubular health (C) with the composite CKD outcome in 656 participants with AKI in the ASSESS-AKI cohort. Cox proportional hazard regression models were adjusted for biomarker at hospitalization, age, sex, race, Hispanic ethnicity, hypertension, diabetes, atherosclerotic disease, congestive heart failure, smoking status, baseline eGFR, albuminuria at hospitalization, urine creatinine at hospitalization, and the slope of urine creatinine from hospitalization to 12 months after discharge. Follow-up started at 12 months after hospitalization, and participants who died were censored. Median follow-up duration was 4.3 years.