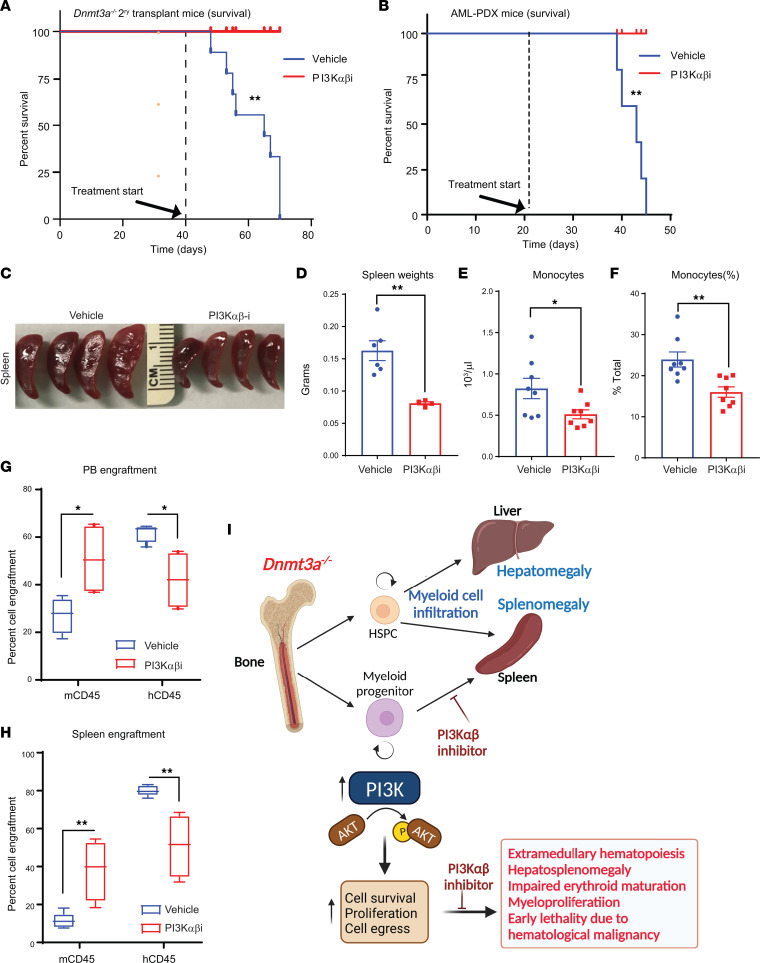
Figure 12. PI3K inhibitor treatment of mice bearing human AML cells bearing DNMT3A mutation enhances their survival.
(A) Secondary recipients of Dnmt3a–/– BM cells were prepared for the survival study by injecting 2 × 106 of Dnmt3a–/– cells from primary BM transplants of Dnmt3a–/– cells. Six weeks after transplantation, these mice were treated with the PI3K inhibitor (Bay1082439) for 21 days (75 mg/kg body weight). As seen in A, all mice belonging to the vehicle group succumbed by day 70 after transplant, whereas none of the drug-treated mice died within this time period. n = 9, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, P < 0.003. (B) Patient-derived AML cells (1 million) bearing DNMT3A mutation were transplanted into NSG-cyto mice to generate AML-PDX. Starting day 20 after transplant, these mice were treated with vehicle or PI3K αβ inhibitor for 21 days. As seen in B, all mice belonging to the vehicle group succumbed by day 45 after transplant, whereas none of the drug-treated mice died within this time period. n = 5, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test, P < 0.001. (C) Images of spleens derived from drug- and vehicle-treated mice. (D) Quantitative analysis of spleen weights from vehicle- and drug-treated AML-PDX mice. n = 5, mean ± SEM, unpaired t test (2-tailed), P < 0.001. (E and F) Quantitative analysis of the number of monocytes in vehicle- versus drug-treated mice. n = 8, mean ± SEM, unpaired t test (2-tailed), *P = 0.05, **P = 0.005. (G and H) Quantitative assessment of percent engraftment of murine and human CD45 cells in the PB and spleen of vehicle- and drug-treated mice as assessed by flow cytometry. n = 5–8, 2-way ANOVA, *P = 0.05, **P = 0.005. The boxes shown with lower and upper quartiles separated by the median (horizontal line), and the whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum values. (I) Model illustrating the role of PI3K signaling in Dnmt3a loss–induced myeloid malignancy. PI3Kαβ specific inhibitor blocks the Dnmt3a loss–induced malignant characteristics and improves survival.