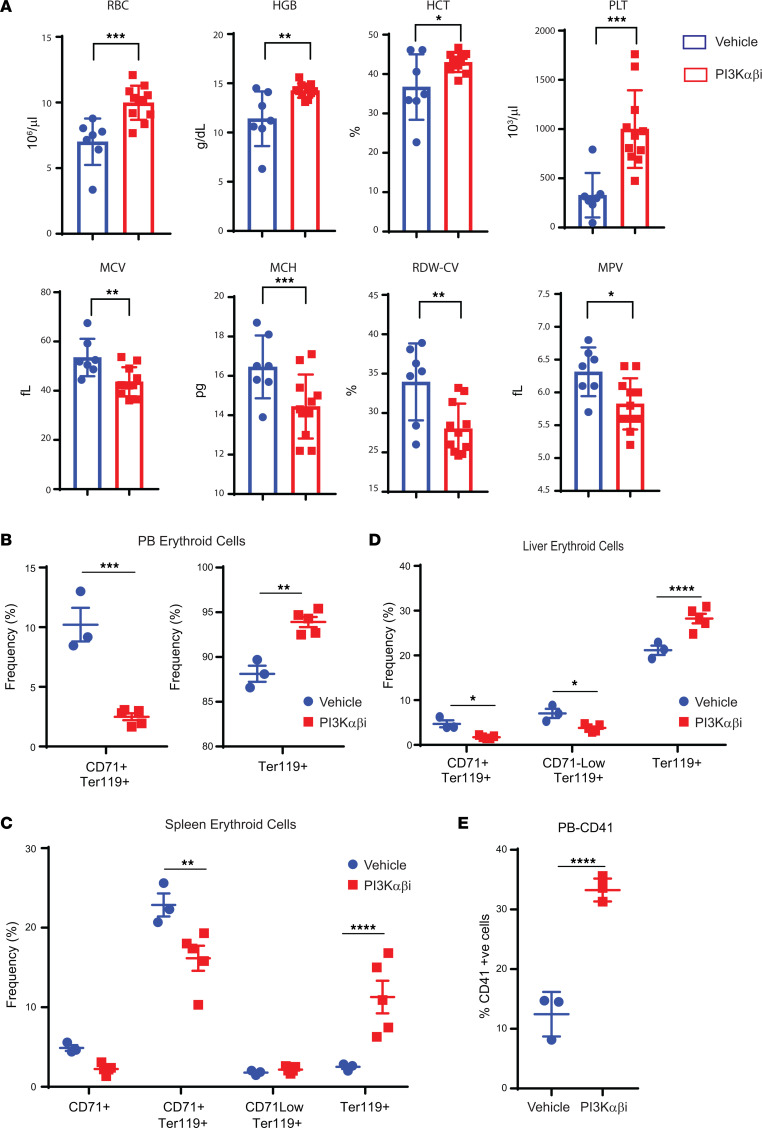
Figure 5. PI3K αβ inhibition improves erythroid cell maturation in mice bearing Dnmt3a–/– malignant cells.
(A) Peripheral red cell parameters in mice transplanted with Dnmt3a–/– BM cells treated with vehicle or the PI3K αβ inhibitor (Bay1082439) for 21 days. n = 7–11, mean ± SEM, *P = 0.05, **P = 0.005, ***P = 0.0005. (B–D) Flow cytometry analysis was performed on PB (B), spleen (C), or liver cells (D) from mice transplanted with Dnmt3a–/– cells and treated with the PI3K αβ inhibitor as in A. Quantitative data showing CD71+Ter119+ immature erythroid cells, CD71loTer119+ immature erythroid cells, and Ter119+ mature erythroid cells in vehicle- and PI3K αβ inhibitor–treated mice. n = 3–5, mean ± SEM, *P = 0.05, **P = 0.005, ***P = 0.0005, ****P = 0.00005. (E) Quantitative data showing increased presence of mature platelets in the PB of drug-treated mice compared with controls. n = 3–5, mean ± SEM, ****P = 0.00005. Unpaired t test (2-tailed) was performed in A, B, and E. Two-way ANOVA (Sidak’s multiple comparison) was performed in D and E.