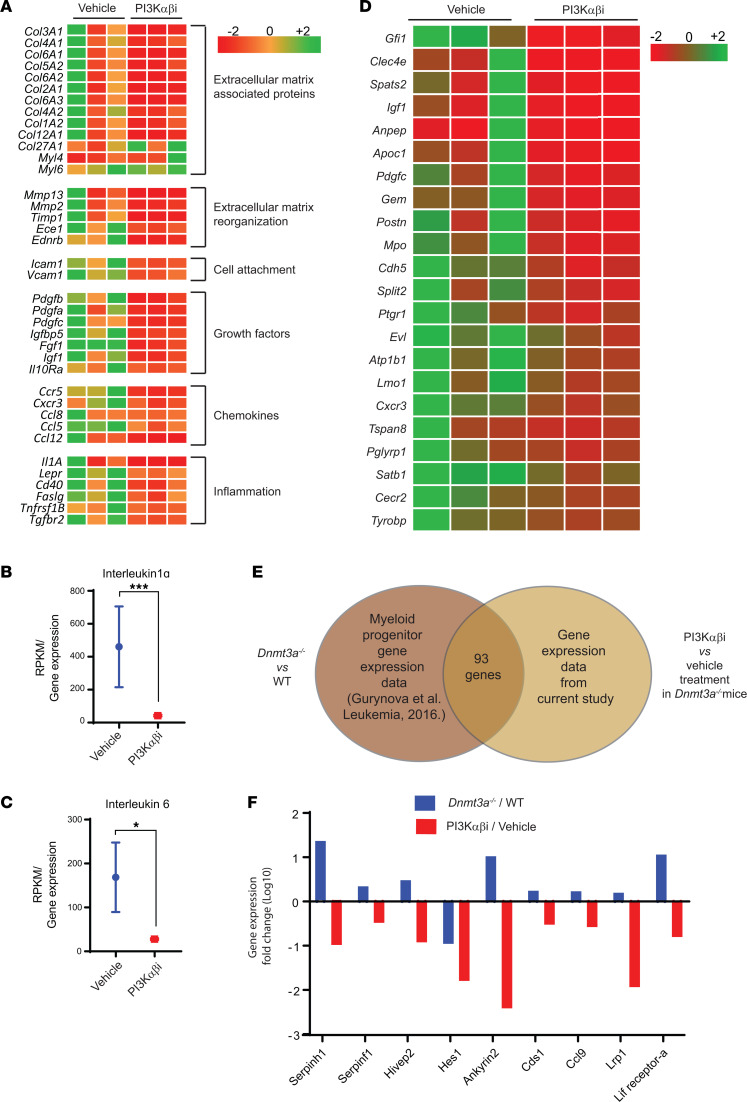
Figure 8. PI3K inhibition reverts Dnmt3a loss–induced changes in the expression of genes involved in cell migration and inflammation and alters the expression of fetal liver HSC genes.
BM cells were collected from vehicle or PI3K αβ inhibitor–treated mice bearing Dnmt3a–/– malignant cells. RNA was isolated and subjected to next-generation sequencing, and gene expression analysis was performed. (A) Heatmap showing that PI3K αβ inhibitor treatment reduces the expression of genes involved in cell motility, cell attachment, inflammatory cytokines, and chemokines. (B and C) Quantitative assessment of the level of expression of IL-1α and IL-6 in drug-treated mice versus controls. n = 3, mean ± SEM, EdgeR DE analysis, *P = 0.05, ***P = 0.0005. (D) Heatmap showing gene expression involved in the development of fetal liver HSCs downregulated as a result of PI3K αβ inhibitor treatment in the Dnmt3a–/– cells versus controls. (E and F) Analysis of GMP progenitor gene expression data from a study involving Dnmt3a–/– and WT mice (13) was compared with the BM-derived gene expression data in the current study from vehicle- and PI3K αβ inhibitor–treated mice bearing Dnmt3a–/– cells. Venn diagram shows that 93 genes were found to be differentially regulated in both data sets. Comparative assessment of gene expression fold changes of indicated genes (F) in Dnmt3a–/–/WT and PI3Kαβ/vehicle treatment groups.