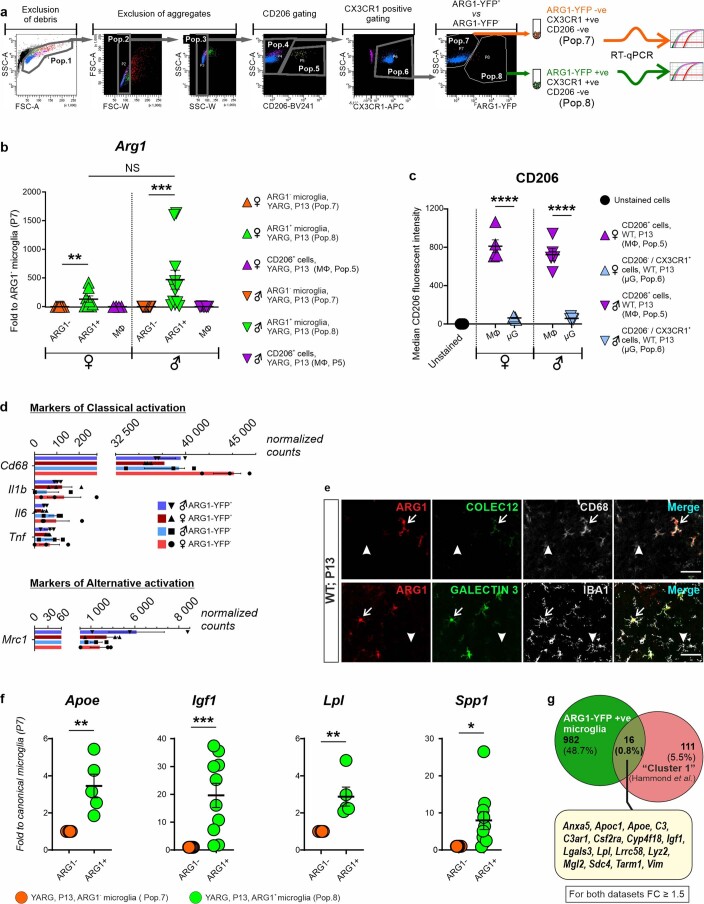
Extended Data Fig. 7. P13 Arg1+microglia cannot be classified as either classical or alternative activated microglia.
a, Gating strategy for RT-qPCR was identical to gating for sorting prior to RNA-Seq (Extended Data Fig. 5a). b, RT-qPCR indicates that Arg1 gene expression is restricted to the ARG1-YFP + /CX3CR1-/CD206− (Pop.8) population. Three to five brains were dissected from either female or male animals per biological replicate (females, n = 8 litters; males, n = 12 litters). Female, ARG1negative - ARG1positive, P = 0.0096; male, ARG1negative - ARG1positive, P < 0.0001. c, Microglia (μG) are known to express low levels of Mrc1 (gene expressing CD206) (a, reference84), in substantially lower levels than macrophages (MΦ) (females, n = 6 litters; males, n = 5 litters). Female, macrophages - microglia, P < 0.0001; male, macrophages - microglia, P < 0.0001. d, Although ARG1 is long been considered a marker of alternative activation, P13 Arg1+microglia (and P13 Arg1-negative-microglia), express both classical and alternative activation markers (females, n = 3 litters; males, n = 3 litters, data derived from RNA-Seq). e-f, Differentially expressed genes from RNA-Seq validated by immunohistochemistry (representative image from 3 female animals) (e) and RT-qPCR (n= min. 5 litters) (f). Apoe, P = 0.0049; Igf1, P = 0.0005; Lpl, P = 0.0062; Spp1, P = 0.0101. Scale bars, 50 μm. g, Venn diagram showing overlaps between Arg1+microglia and Arg1-negative-microglia presented here and “cluster 1” (reference17) (FC ≥ 1.5). Note: only validated genes have been included in this list. Data in b, c and f are represented as mean ± s.e.m. Statistical significances were determined by Kruskal-Wallis test (b, Arg1), ANOVA (c, CD206), and unpaired t tests (f); all P-values are two-sided, and P-values for multiple comparisons were corrected using Dunn’s method (b) and Bonferroni’s method (c), respectively. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001, n.s. indicates not significant.