Fig. 1.
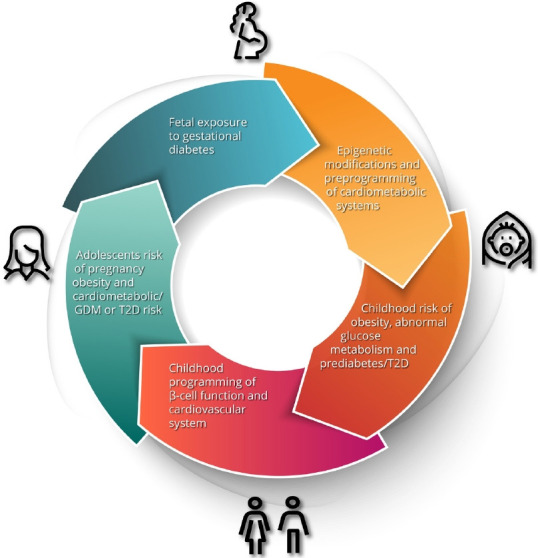
The intergenerational impact of gestational diabetes. Maternal hyperglycemia and resultant fetal hyperinsulinism results in developmental and epigenetic preprogramming of cardiometabolic risk in the offspring including obesity, dysglycemia, dyslipidemia, hypertension and early renal dysfunction. These risks progress to evident cardiometabolic abnormalities in adolescents and predispose young women to the development of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) in pregnancy, thereby restarting the cycle. T2D, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
