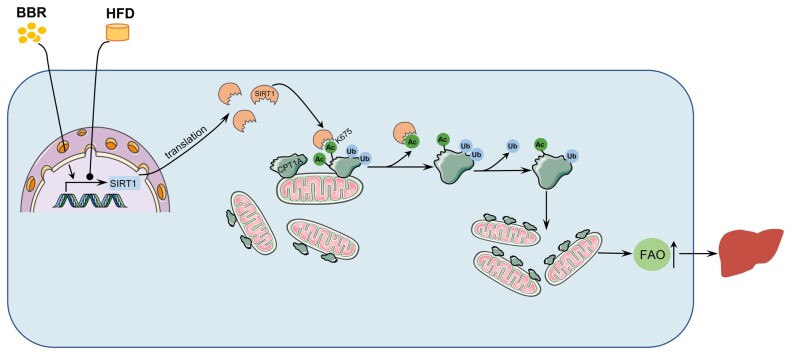
Graphical Abstract.
The mechanism of BBR in ameliorating non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis. BBR increased the expression of SIRT1. SIRT1 deacetylated CPT1A at the Lys675 site, which suppressed the ubiquitination degradation of CPT1A. The increased CPT1A promoted fatty acid oxidation, thus alleviating non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis. BBR, berberine; HFD, high-fat diet; Ac, acetylation; Ub, ubiquitin; FAO, fatty acid oxidation.