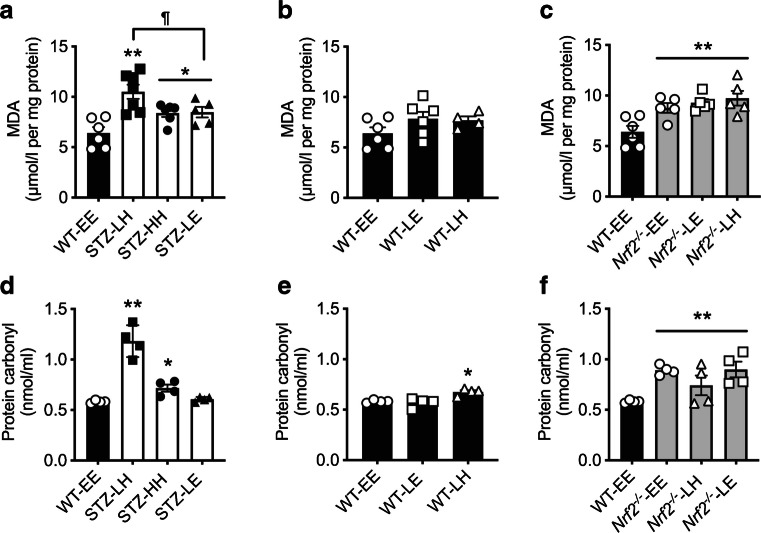
Fig. 2.
Chronic hyperglycaemia is associated with hippocampal oxidative damage. (a) Levels of hippocampal lipid peroxidation were increased in STZ-diabetic mice (white bars) compared with control (WT) mice (black bars) maintained at euglycaemia. (b) Euglycaemic control mice exposed to an acute episode of hypoglycaemia exhibited no change in hippocampal lipid peroxidation. (c) Euglycaemic Nrf2−/− mice (grey bars) displayed increased levels of hippocampal lipid peroxidation irrespective of hypoglycaemic challenge. (d) Protein carbonylation levels were elevated in STZ-diabetic mice exposed to hyperglycaemia compared with control mice at euglycaemia. (e) Control WT mice exposed to an acute hypoglycaemic episode showed a rise in protein carbonylation only when recovered to a hyperglycaemic state. (f) Nrf2−/− mice displayed increased levels of protein carbonylation irrespective of glycaemic variability. n=4–7/group. Results represent mean values ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 vs WT-EE; ¶p<0.05 vs STZ-diabetes (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test). E, euglycaemia; H, high, hyperglycaemia; L, low, hypoglycaemia; MDA, malondialdehyde