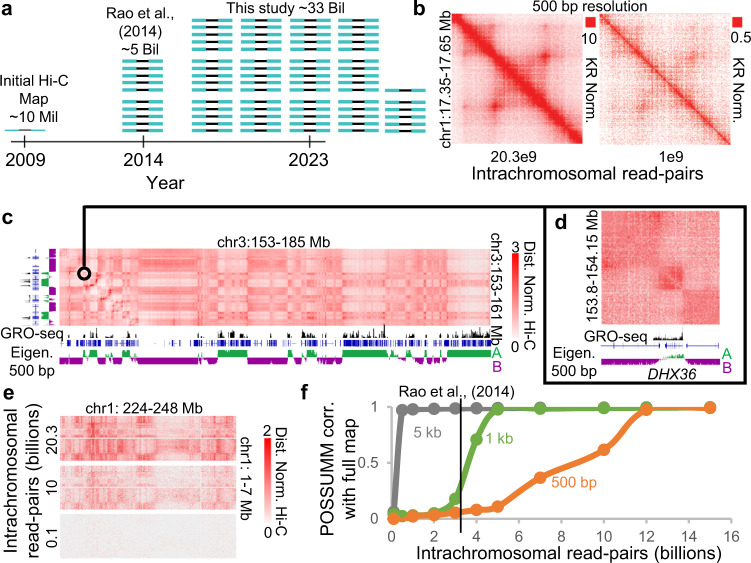
Fig. 1. By combining ultra-deep Hi-C and POSSUMM, we generated a fine map of nuclear compartmentalization achieving 500 bp resolution.
a Schematic representing the total mapped read-pairs in the current study compared to earlier published Hi-C studies. b Example locus showing Hi-C signal in 500 bp bins in our full map with 20.3 billion intrachromosomal read-pairs (left) and when read-pairs are subsampled to 1 billion (right). Scales are set to be proportional to sequencing depth. c Example of compartment interactions in a Hi-C map identified by the eigenvector (Eigen.) in 500 bp bins (bottom track). The black track displays transcription measured by GRO-seq. The black square represents the region shown in Fig. 1d. Scales represent distance normalized Hi-C. d Zoomed in view of a compartment domain. e Long-range Hi-C signal displaying how sequencing depth impacts the visibility of the long-range compartmental checkerboard pattern. f Correlation of the eigenvector in the full map compared to various sequencing depths. The black line indicates the number of intra-chromosomal read pairs in the published GM12878 dataset2. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.