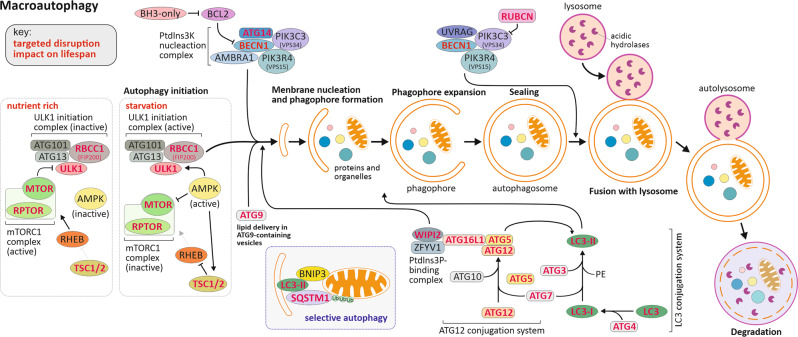
Fig. 2. The autophagy core machinery with indication of which components manipulation have been shown to impact on longevity in various organisms.
Bulk autophagy starts with the stepwise engulfment of cytoplasmic material by the phagophore, which matures into a double-layered vesicle named an autophagosome. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK/PRKAA2) and MTOR-containing mTORC1 complex promote and repress autophagy induction, respectively, through phosphorylation of ULK1 (unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase-1) at distinct residues. Under nutrient rich conditions, AMPK is inactive but mTORC1 is active and phosphorylates and inactivates ULK1. When nutrient starvation occurs, AMPK is activated and mTORC1 is inhibited by AMPK through the phosphorylation of TSC1/2 (TSC complex subunit 1/2) and RPTOR/RAPTOR (Regulator-associated protein of MTOR). Subsequently, ULK1 can interact with and be activated by AMPK-mediated phosphorylation, thereby initiating autophagy. Activation of the ULK1-containing initiation complex triggers phagophore formation by phosphorylating components of the BECN1 (Beclin-1) and ATG14-containing class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (Ptdlns3K) nucleation complex. The activated Ptdlns3K nucleation complex generates PtdIns3P, which leads to the recruitment of the effector proteins WIPI2 (WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting protein 2) and ZFYV1 (Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 1). The expansion of the phagophore requires two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems. The ATG12-conjugation system that supports in the formation of ATG12–ATG5-ATG16L1 ternary complex, which in turn promotes the second conjugation reaction. The second system, the LC3 conjugation system, involves the conjugation of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to MAP1LC3/LC3 (microtubule associated protein 1 light chain 3, in mammals). Lipid conjugation converts the soluble form of LC3-I into a phagophore membrane-bound LC3-II form that functions in phagophore expansion, and in cargo recognition of ubiquitinated proteins and organelles, including upon selective autophagy with the involvement of autophagy receptors, e.g. BNIP3 (BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3), and Ub-dependent autophagy receptors, e.g. SQSTM1/p62 (Sequestosome-1). As a result of membrane expansion and sealing, the autophagic cargo becomes sequestered within the autophagosome. Autophagy completion involves the fusion of the mature autophagosome with a vacuole or lysosome. An alternative Ptdlns3K complex containing UVRAG (UV radiation resistance-associated gene protein), negatively regulated by RUBCN/RUBICON (Run domain Beclin-1-interacting cysteine-rich domain-containing protein), has been reported to regulate the processes of fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes. Docking and fusion of the outer autophagosomal membrane with that of the lysosome exposes the inner vesicle to the lysosomal lumen, where acidic hydrolases degrade and recycle the macromolecular components for cellular use. Key: Component of the autophagic machinery whose alterations are reported to impact on lifespan are highlighted with red bold text.