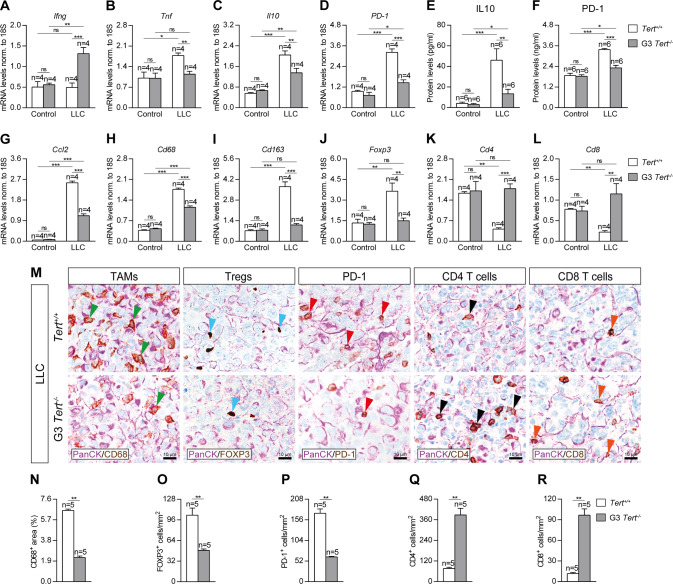
Fig. 3. Telomerase deficiency in the tumor microenvironment decreases expression of lung inflammation and tumor immunosupression markers.
Lung tissue mRNA expression levels of Ifng (anti-tumor immunity) (A), Tnf (Th1 inflammation) (B), and Il10 and PD-1 (tumor immunosupression) (C, D) normalized to 18S expression, and IL10 (E) and PD-1 (F) protein levels in lung homogenates from Tert+/+ and G3 Tert−/− mice. Lung tissue mRNA expression levels of Ccl2 (macrophage chemotaxis) (G), Cd68 (tumor associated macrophages (TAMs)) (H), Cd163 (M2 TAMs) (I), Foxp3 (regulatory T cells (Tregs)) (J), Cd4 (CD4+ helper T cells) (K) and Cd8 (CD8+ cytotoxic T cells) (L) normalized to 18S expression in Tert+/+ and G3 Tert−/− mice. Representative lung immunostainings for PanCK (purple) with CD68 (brown; green arrowheads indicate CD68+ cells), FOXP3 (brown; blue arrowheads indicate FOXP3+ cells), PD-1 (brown; red arrowheads indicate PD-1+ cells), CD4 (brown; black arrowheads indicate CD4+ cells), and CD8 (brown; orange arrowheads indicate CD8+ cells) (M), and quantification of CD68 positive area (N), and number of FOXP3 (O), PD-1 (P), CD4 (Q) and CD8 (R) positive cells/mm2 in LLC-challenged Tert+/+ and G3 Tert−/− mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM (the number of mice is indicated in each case). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001 (Dunn–Sidak test for multiple comparisons and Mann–Whitney or unpaired t tests to compare 2 independent groups).