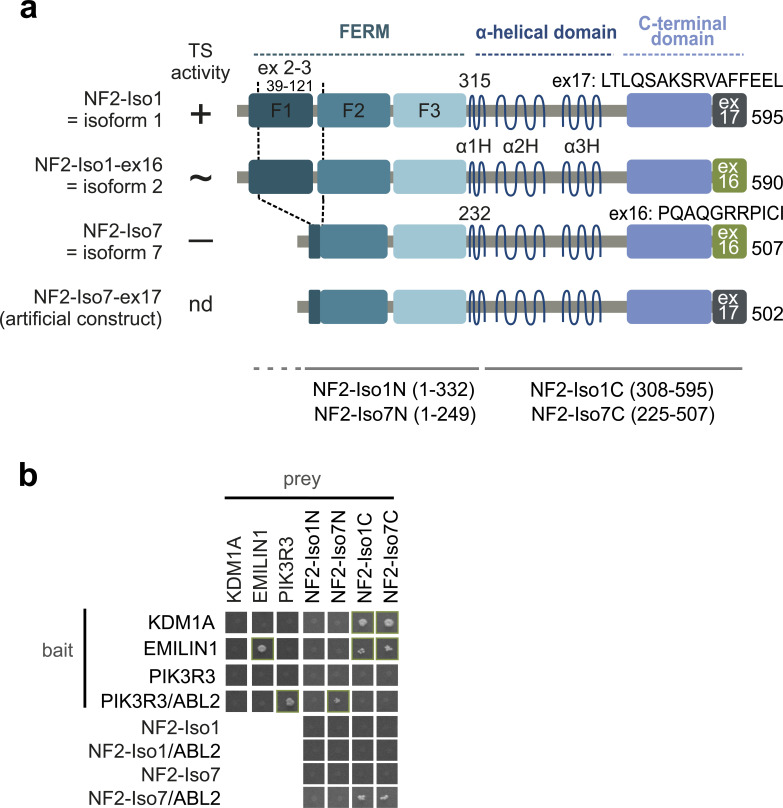
Figure S1. NF2 splice isoforms and constructs used in Y2H analyses.
(Related to Fig 1): (A) NF2 splice isoforms and constructs used in the study. The canonical isoform 1 is 595 AA long and contains exon 17 (P35240-1). It includes all features of isoforms 2 and 7 except for differences in the C-terminal end from amino acids 580–595. Isoform 2 (P35240-2) has a length of 590 amino acids and differs in the C-terminal end derived by alternative splicing of exon 16 instead of exon 17 from isoform 1. Isoform 7 is a shorter splice isoform with 507 amino acids, lacking most of the F1 FERM subdomain and the beginning of the F2 subdomain (exons 2 and 3, AA 39–121, P35240-4). As for isoform 2, the C-terminal end consists of exon 16. Several other splice isoforms were described, in addition to the three isoforms depicted; however, NF2-Iso7-ex17 is an artificial construct to test the influence of the isoform 1 C-terminus on the interactions with the shorter isoform 7. Constructs representing the N-terminal and C-terminal halves of NF2 are indicated. Tumor suppressor activity (TS activity) was demonstrated for isoform 1 (+) but not for isoform 7 (−); nd = not determined. (B) Y2H protein interaction results. Y2H mapping of NF2-interacting regions. Growth on selective agar, indicating protein interaction is shown. KDM1A and EMILIN1 both interacted with the NF2 C-terminal halves, independently of whether the last amino acids resemble isoform 1 or isoform 7, PIK3R3 interacted with the N-terminal NF2-Iso7N construct. NF2-Iso1N and NF2-Iso7N when used as prey did not interact with full-length NF2 constructs. EMILIN1 formed homo-dimers and PIK3R3 formed a homodimeric interaction in the presence of an active tyrosine kinase ABL2. This requirement for a human tyrosine kinase explains the requirement for ABL2 for the interaction of PIK3R3 with WT NF2-Iso7N, the N-terminal half of isoform 7. The reverse bait–prey configuration of the experiment is shown in Fig 1. Please note that NF2-Iso1C, NF2-Iso7C were autoactive when used as bait and were therefore excluded from the analysis.