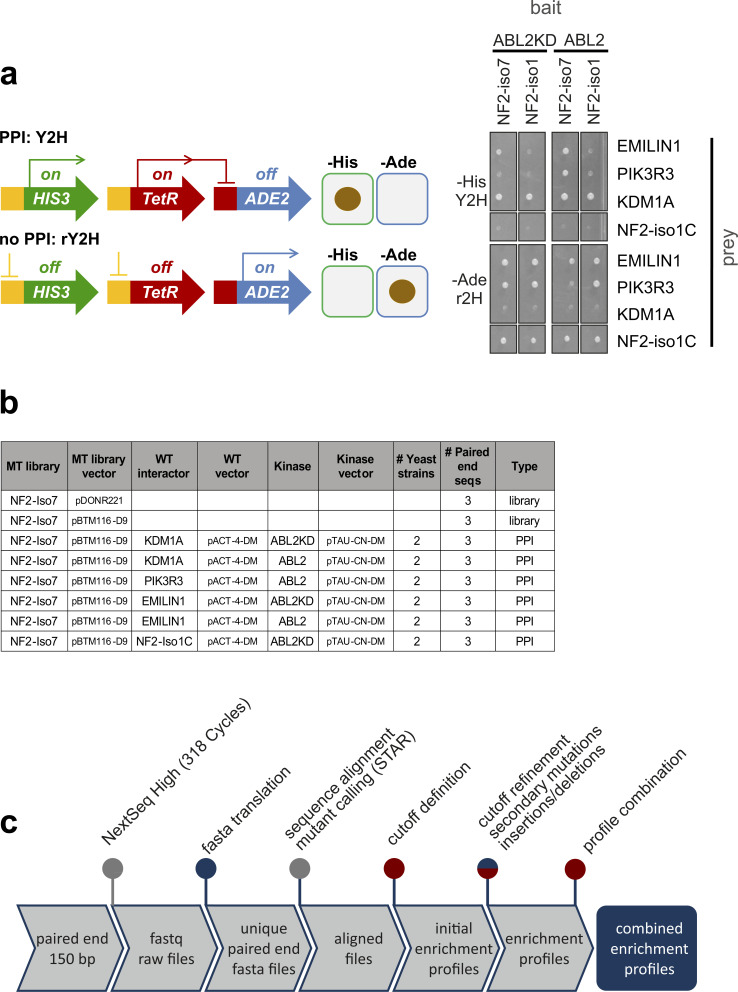
Figure S2. Reverse-Y2H protein interaction pertrubation analyses of NF2.
(Related to Fig 2): (A) Reverse Y2H analysis. Genetics of reverse-Y2H strain (left). A bait–prey pair can be assayed for interactions on selective agar lacking histidine or lacking adenine, respectively. Interacting bait–prey pairs grow on agar lacking histidine (-his) and noninteracting pairs grown on agar lacking adenine (-ade). When using a deep mutational scanning pool representing all single amino acid exchanges in the place of one partner, noninteracting variants can be selected on agar lacking adenine. A representative growth experiment (right) growing the strains on the two agar plates, lacking adenine (rY2H) or histidine (Y2H), respectively. (B) Overview of the rY2H deep mutagenesis interaction experiments and the sequencing runs used for evaluation. All MT libraries generated were sequenced three times in the entry vector and in the yeast expression vector as controls. The controls did not face selection pressure and the combined sequence read count was used as baseline for the enrichment analysis of the rY2H interactions. The rY2H interactions were tested in two yeast strain pairs and three biological replicates were individually sequenced resulting in a total of six sequencing runs per interaction. (C) Sequence analysis pipeline for the generation of mutant enrichment profiles. Blue dots represent Perl scripts, red dots indicate R script used in the analysis step. Sequence alignment and mutant calling was done with the STAR package.