Figure 2. C‐CSP specific mAbs are frequently encoded by IGHV3‐21 .
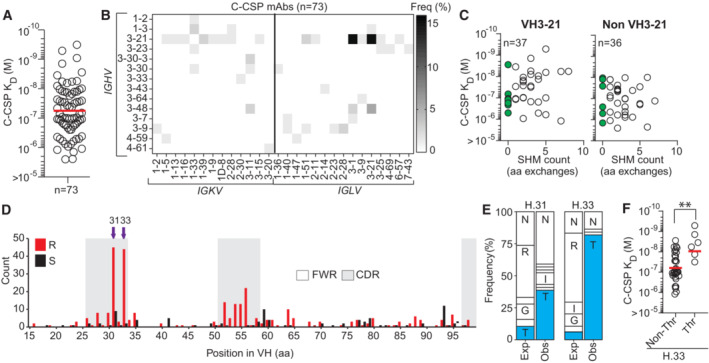
- SPR affinity of C‐CSP reactive mAbs.
- Frequency of mAbs encoded by the indicated IGHV and IGKV or IGLV pairs.
- VH SHM load of VH3‐21 and non‐VH3‐21 mAbs. mAbs with unmutated VH are highlighted in green; n indicates the number of mAbs tested.
- Amino acid (aa) VH replacement (red bars) and silent (black bars) SHM in VH3‐21 mAbs (n = 113). FWR, framework region; CDR, complementarity‐determining region.
- C‐CSP affinity for selected VH3‐21 mAbs with or without Thr mutation at position H.33.
Data information: The statistical significance in (F) was assessed by two‐tailed Mann–Whitney test: **P = 0.0019. Red horizontal lines in (A, F) indicate geometric mean values. Data in (A, C and F) are representative of two independent technical replicates.
Source data are available online for this figure.
