Figure 1: E3311 validation and benchmarking study framework.
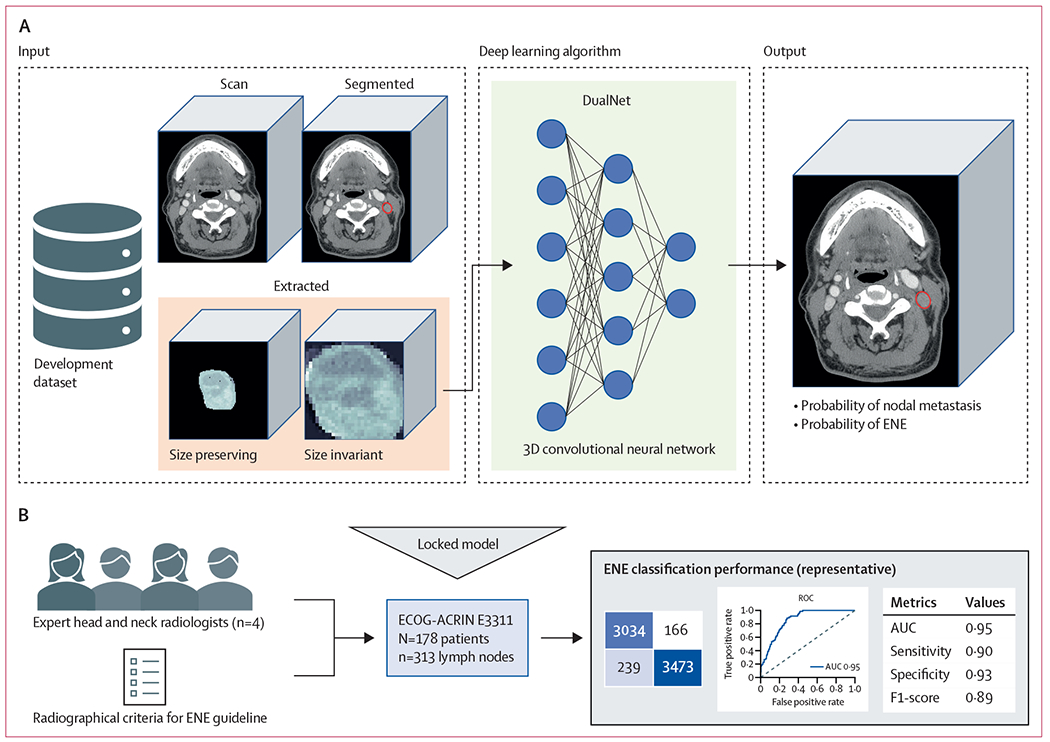
(A) The previously developed deep learning algorithm was retrained on a combined, multi-institutional dataset from three sources to predict probability of nodal metastasis and ENE on a node-by-node basis. (B) The model was locked and tested on a curated dataset of 313 lymph nodes from 178 patients enrolled on the E3311 de-escalation trial for patient withs human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal carcinoma, a trial that specifically excluded radiographic matted nodes or overt clinical ENE. Four expert head and neck radiologists from National Comprehensive Cancer Network comprehensive cancer centers, and with access to a validated educational guideline for radiographic ENE criteria, individually reviewed the lymph nodes, and made a prediction of node positivity or ENE on a forced Likert scale. ENE classification performance was compared between the deep learning algorithm and the radiologists, with a primary endpoint of area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. 3D=three dimensional. AUC=area under curve. ECOG-ACRIN=Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group and the American College of Radiology Imaging Network. ENE=extranodal extension. ROC=receiver operating characteristic.
