Fig. 8.
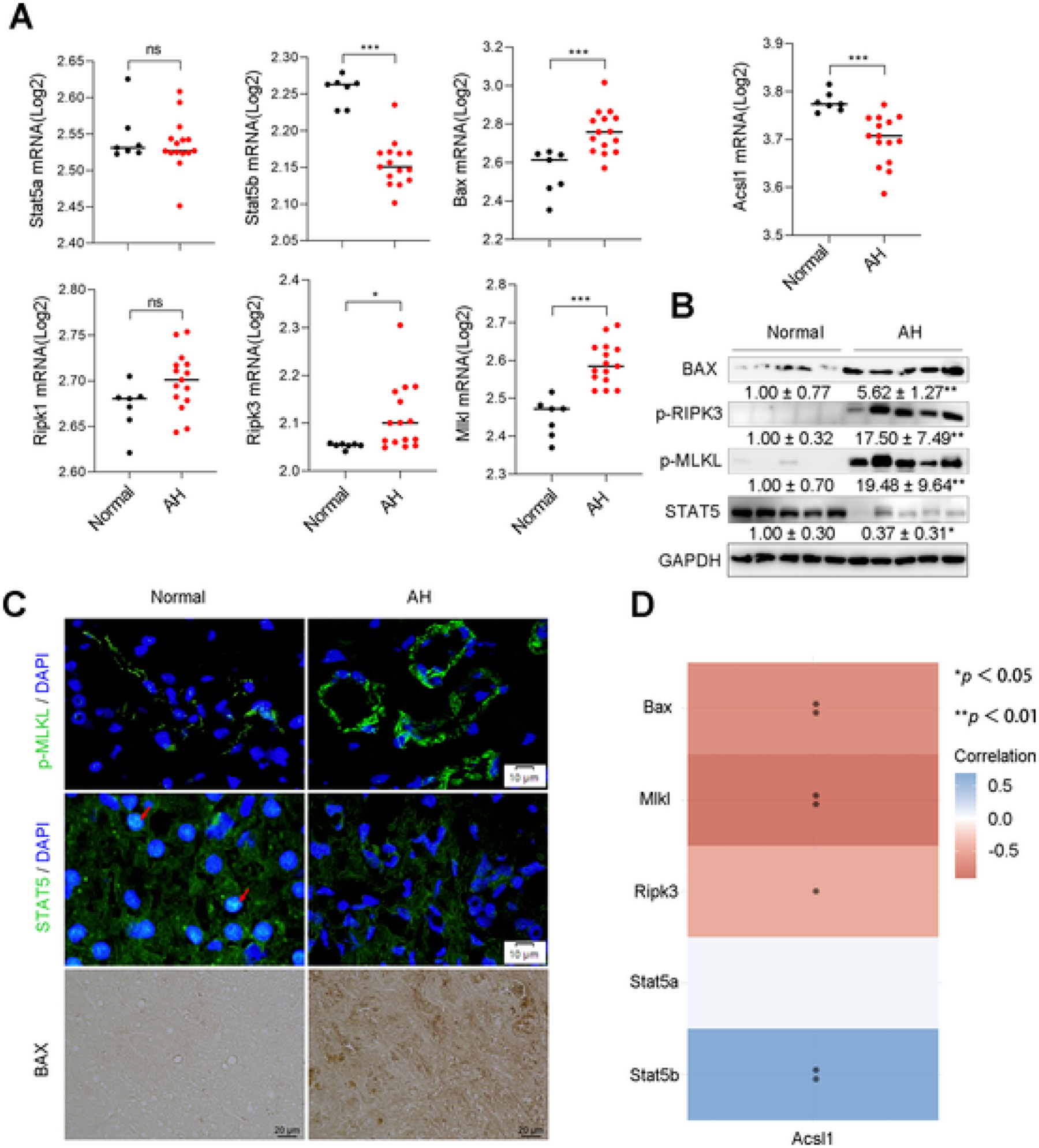
STAT5-ACSL1 signaling mediated liver injury in patients with alcoholic hepatitis. (A) The RNA-seq analysis of Stat5a, Stat5b, Acsl1, Bax, Ripk1, Ripk3, and Mlkl in liver tissues from normal subjects (Normal, n = 7) and patients with alcoholic hepatitis (AH, n = 15). GEO accession number: GSE28619, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (B) Western blot assay of hepatic proteins related to STAT5-ACSL1signaling and cell death markers in the liver of normal subjects (Normal, n = 5) and AH patients (AH, n = 5). (C) IF staining of p-MLKL and SATAT5 (Scale bars = 10 μm.), and IHC staining of BAX (Scale bars = 20 μm.) on liver tissue sections from normal subjects and AH patients. Arrows in red indicate the nuclear localization of STAT5. (D) A heatmap of correlative analysis of mRNA levels of Acsl1 with Stat5, apoptotic gene Bax and necroptotic genes including Mlkl and Ripk3. The abscissa and ordinate represent genes, different colors represent different correlation coefficients (blue represents positive correlation whereas red represents negative correlation), the darker the color, the stronger the relation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, values with different superscripts are significantly different.
