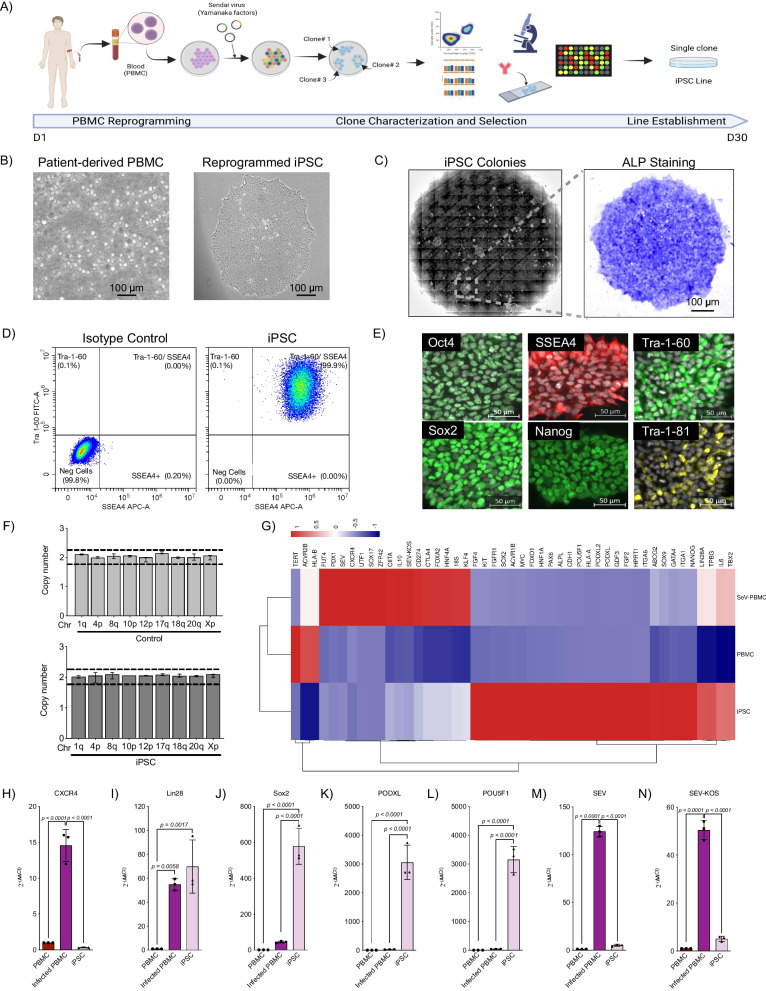
Fig. 1.
Establishment of iPSC line from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. A Overview of processes for generating an induced pluripotent stem cell line including patient blood collection (day 1), peripheral blood mononuclear cell isolation, infection with Yamanaka factors, optimal clone selection, and iPSC line establishment (day 30). B Microscopy of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and established iPSCs. C Characterization of pluripotency of the established iPSC line using alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining. D Flow cytometric analysis of the selected iPSC line with isotype control and characterization of Tra-1-60 and SSEA4 expression. E Immunohistochemistry of the established iPSC line with expression of Oct4, Sox2, SSEA4, and Tra-1–60. F Quantitative PCR evaluation of the established iPSC line frequently for genetic abnormalities within iPSCs comparing to commercially available control DNA (n = 9, 3 per iPSC line) G Genetic microarray results comparing established iPSCs to fibroblasts and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (n = 3, 1 per iPSC line) H Differential expression of CXCR4, I Lin28, J Sox2, K PODXL, L POU5F1, M SEV and N SEV-KOS in PBMC, infected PBMC and iPSC (n = 3)