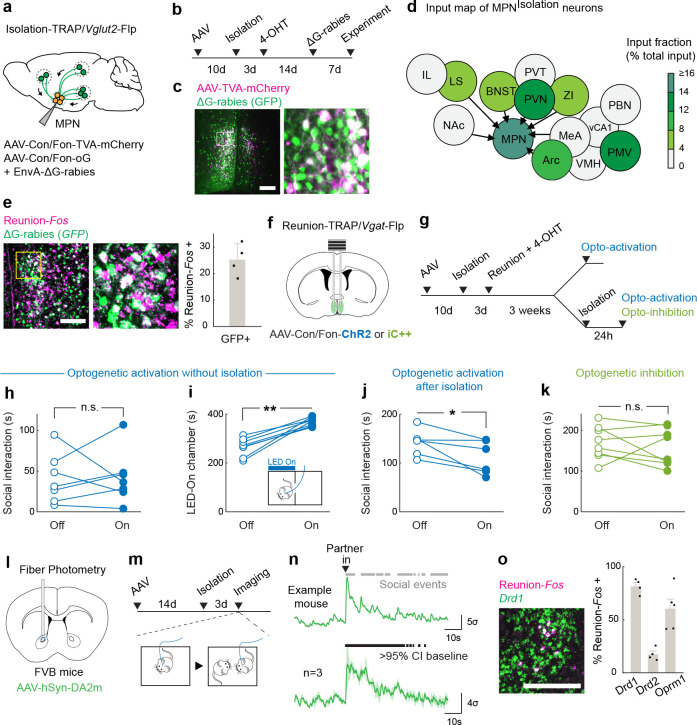
Figure 4. MPNReunion neurons modulate social satiety.
a-b, Intersectional (Cre/Flp) viral tracing strategy to map input brain regions of MPNIsolation neurons. c-d, Representative image of MPNisolation starter neurons (c) and input brain regions (d). (LS, lateral septum. IL, infralimbic cortex. NAc, nucleus accumbens. BNST, bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. PVN, paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus. ZI, zona incerta. Arc, arcuate nucleus. VMH, ventromedial hypothalamus. MeA, medial amygdala. PMV, ventral premammillary nucleus. vCA1, ventral hippocampal CA1. PBN, parabrachial nucleus) e, Representative image and quantification of MPNReunion neurons input into MPNIsolation neurons, n=4. f-g, Intersectional (Cre/Flp) strategy to target MPNReunion neurons for optogenetic manipulations. h-j, Behavioral effects of optogenetic activation of MPNReunion neurons in different conditions: without isolation (h), n=7; after isolation (j), n=6; and real-time place preference test (i), n=7. k, Behavioral effects of optogenetic inhibition of MPNReunion neurons during social reunion, n=8. l-m, Experimental strategy to record dopamine release in NAc during social reunion. n, Dopamine release in NAc upon social reunion, n=3. Gray bars (upper) indicate social events and black bars (lower) indicate the significance of enhanced activity above 95% confidence interval (CI) of the baseline. o, Cell type identification of NAc neurons activated during reunion, n=4–5. h-k, Wilcoxon signed-rank tests; n.s., not significant; *p<0.05, **p<0.01. Shaded areas and all error bars represent the mean ± s.e.m. All scale bars, 200μm.