Figure 5. Identification of the structural binding epitope in BabA for the broadly blocking ABbA.
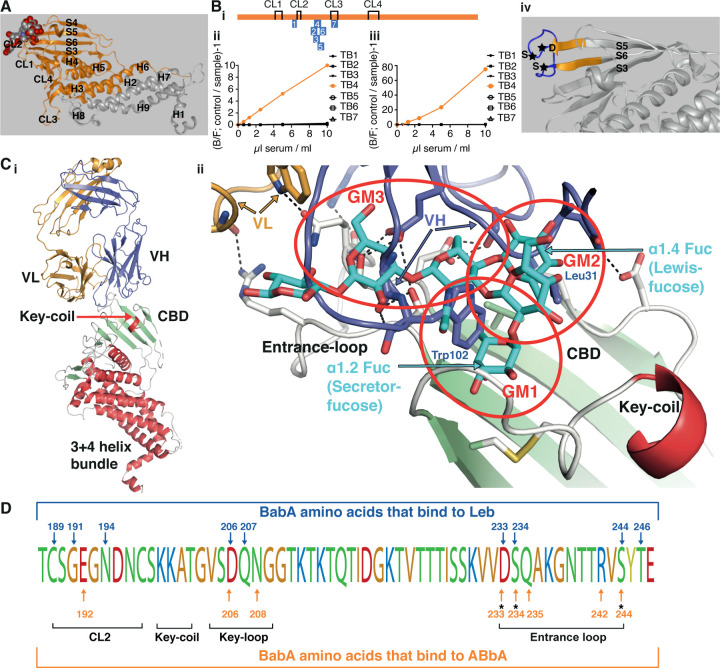
(A) The aa76–335 BabA fragment in orange was superimposed on the 460 aa BabA structure (grey) constituting the minimal 260 aa BabA domain required for ABbA binding. The Leb glycan in red/grey spheres indicates the CBD location.
(Bi) The schematic locations of the seven BabA peptides (TB1–7) derived from strain 17875/Leb used to raise rabbit anti-sera. The four disulfide loops (CL) are indicated for orientation (Figure S5B).
(Bii) Inhibition of ABbA binding and (Biii) inhibition of Leb binding to 17875/Leb bacterial cells was tested with the seven rabbit sera in the dilution series.
(Biv) The TB4 (BabA230–247) peptide includes the Entrance loop (blue) to the CBD, where the critical D233-S234-S244 (DSS) residues are indicated by stars, and the proximal parts of the connecting β-strands S5 and S6 are shown in orange.
(Ci) Co-crystal of ABbA-Fab and BabA with the locations of the ABbA Light (VL) (orange) and Heavy (VH) (lilac) chains. The CBD (green) and the Key-coil (bright red) are located in the extra-cellular domain i.e., the BabA body domain (red).
(Cii) The ABbA/BabA co-crystal structure with Leb (turquoise) superimposed in the CBD region, with the Key-coil (in red from Ci) for orientation. The ABbA-CBD interactions demonstrate three sites of Leb glycan mimicry, including GM1, where ABbA VH (lilac) replaces the α1–2 “Secretor” fucose in the CL2 pocket; GM2, where ABbA VH replaces the α1–4 “Lewis” fucose; and GM3, where ABbA VH binds to the DSS triad residues.
(D) The 17875/Leb BabA CBD domain with the amino acids positions that bind to Leb and/or to ABbA are indicated by blue vs. orange arrows, respectively.