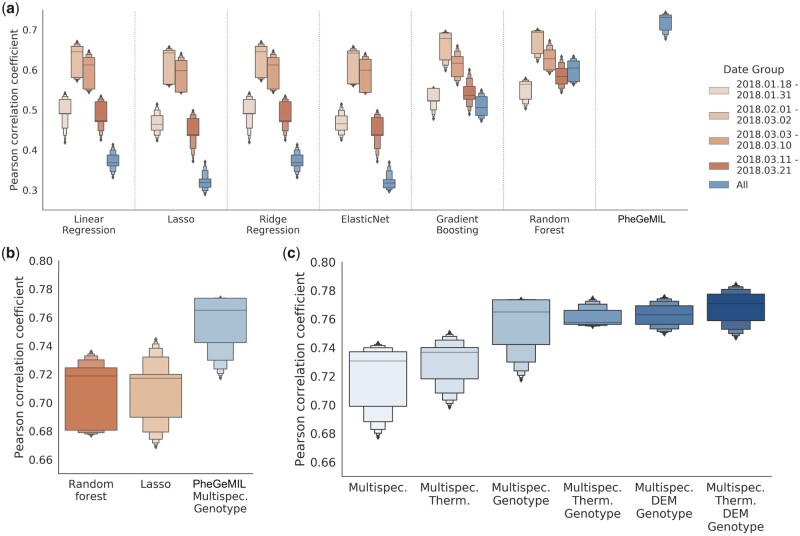
Figure 2.
Performance of deep multiple instance learning (MIL) and genomic selection methods models for yield prediction measured using Pearson correlation coefficient over a 5-fold cross validation scheme. (a) Performance when relying on multispectral images alone. The baseline models use summary statistics of the multispectral channels and of notable vegetation indices computed on the images. Moreover, they are trained on images from different date groups, as images of late-growth stage carry more predictive power. (b) Performance when relying on a combination of multispectral and genotypic input for yield prediction for a nonlinear baseline (Random forest), a linear baseline (Lasso), and PheGeMIL. For the two baseline models, the most informative images were preselected and used for prediction (dates 01 February 2018–02 March 2018, as opposed to all for PheGeMIL). (c) Performance evaluation when adding new data channels in PheGeMIL prediction. Multispectral images are always kept in the comparison, given that they are the basis of the approach. Only a subset of the possible channel combinations is explored, as the focus lies in combining images and genotypic information. MIL, multiple instance learning; DEM, digital elevation models; Multispec., multispectral; Therm., thermal.