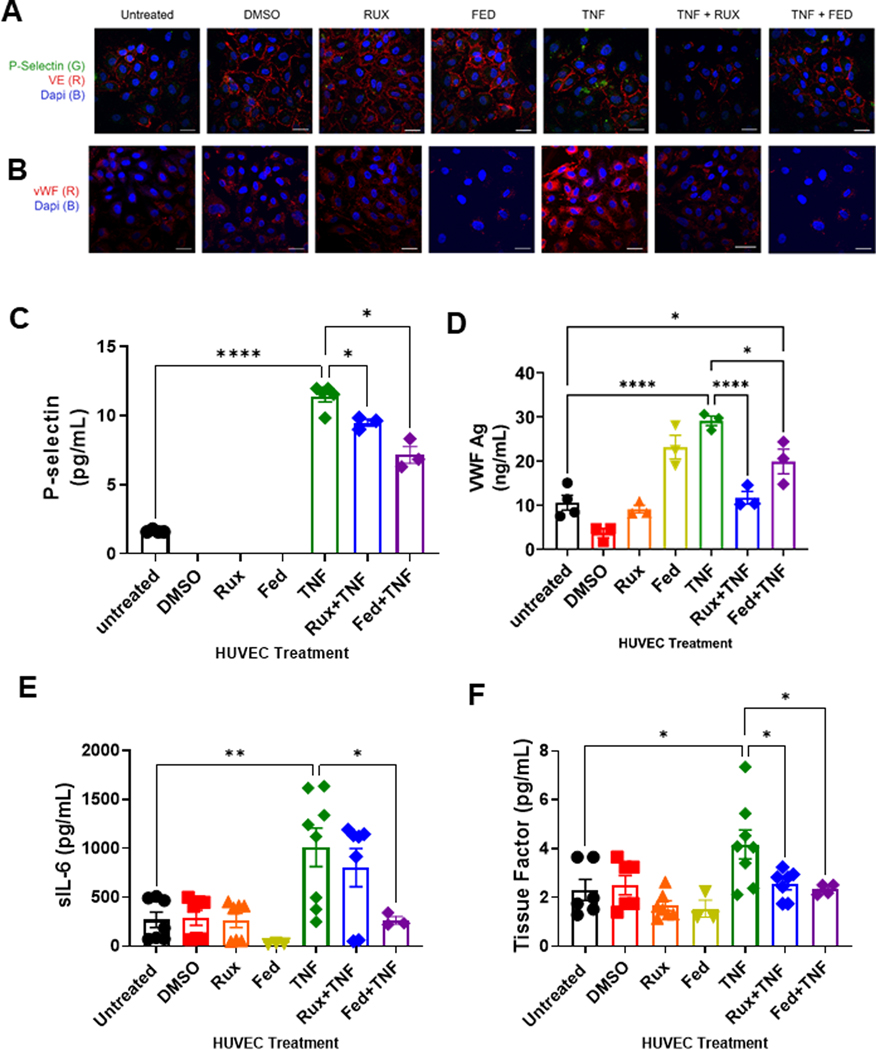
FIGURE 2.
Ruxolitinib and fedratinib decrease TNF-α mediated release of P-selectin and VWF and reduce secretion of IL-6 and tissue factor. HUVEC were treated with 0.4 μM ruxolitinib or 1 μM fedratinib JDB for 30 minutes followed by addition of 10 ng/mL TNF-α for 4 hours. Conditioned media was collected for ELISA. Cells were fixed and stained for the following analyses. (A) Confocal microscopy demonstrating release of P-selectin from endothelial cells. Unpermeablized HUVEC were stained for P-selectin (green) and VE-cadherin (red) and nuclei counterstained with DAPI. (B) Confocal microscopy demonstrating surface expression of VWF. Unpermeablized HUVEC were stained for VWF (red) and nuclei counterstained with DAPI. (C) ELISA assay for soluble P-selectin (sP-selectin). (D) ELISA assay for sVWF antigen. (E) Cytokine array results for sIL-6. (F) Cytokine arrays results for tissue factor. Each dot represents an individual replicate from a total of 3 separate experiments, with n = 2 to 3 replicates per experiment. For sP-selectin, VWF, and sIL-6, several replicates had undetectable levels. Error bars represent mean ±SE of means. p values from analysis of variance testing with appropriate post-hoc multiple comparison testing. ns, not significant. * p < .05, ** p < .01, *** p < .001, **** p < .0001.