Abstract
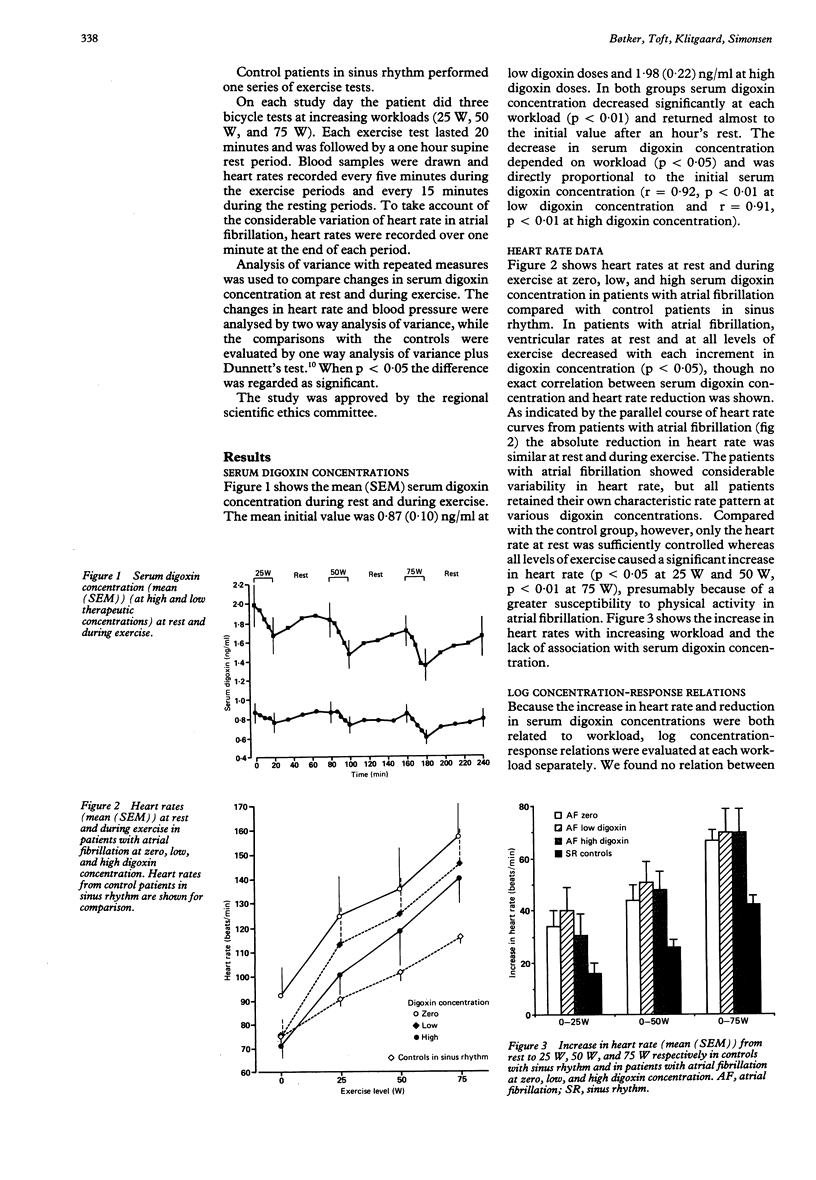
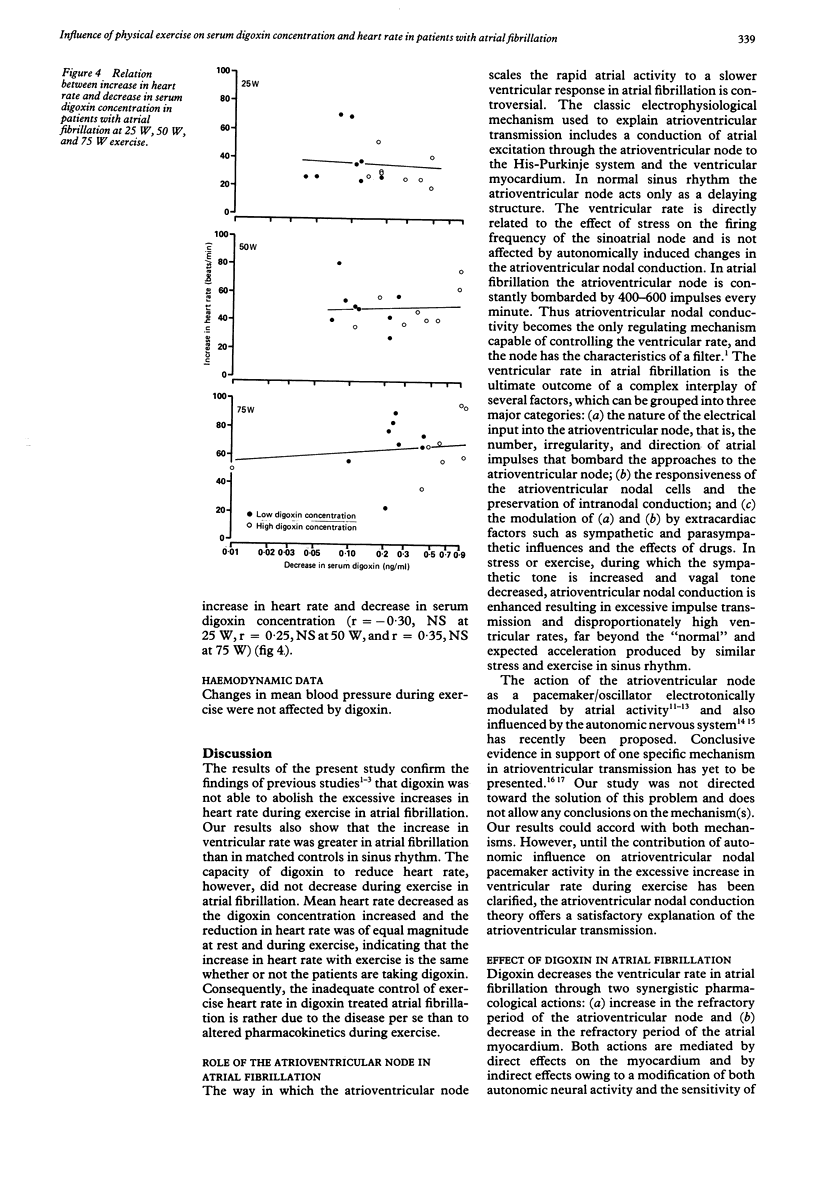
Heart rate and serum digoxin concentration in eight patients with atrial fibrillation were studied at rest and during exercise when initial serum digoxin concentrations were zero and at low and high therapeutic values. Eight patients with ischemic heart disease and in sinus rhythm were studied for comparison. Though the serum digoxin concentration decreased significantly during exercise, the absolute reduction in heart rate was the same at rest and during exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation. Compared with the control patients in sinus rhythm, the heart rate in patients with atrial fibrillation was not adequately controlled during exercise by any serum digoxin concentration tested despite a reduction in heart rate with increasing digoxin concentration. The effects of digoxin on heart rate regulation in atrial fibrillation are complex and include direct effects on the myocardium as well as indirect effects mediated by modulation of the autonomic nervous system; the present results indicate that the drug is not displaced from the target organs by decreasing serum concentrations during exercise. In atrial fibrillation, because the demands on the filter function of the atrioventricular node are highly unphysiological, the effect of digoxin on heart rate during exercise is not adequate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beasley R., Smith D. A., McHaffie D. J. Exercise heart rates at different serum digoxin concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Jan 5;290(6461):9–11. doi: 10.1136/bmj.290.6461.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst C., Meijler F. L. Baroreflex modulation of ventricular rhythm in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1984 Nov;5(11):870–875. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a061585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. W., Goble A. J. Effect of propranolol on exercise tolerance of patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J. 1969 May 3;2(5652):279–280. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5652.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain D. A., White R. J., Howard M. R., Smith T. W. Plasma digoxin concentrations in patients with atrial fibrillation. Br Med J. 1970 Aug 22;3(5720):429–432. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5720.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBianco R., Morganroth J., Freitag J. A., Ronan J. A., Jr, Lindgren K. M., Donohue D. J., Larca L. J., Chadda K. D., Olukotun A. Y. Effects of nadolol on the spontaneous and exercise-provoked heart rate of patients with chronic atrial fibrillation receiving stable dosages of digoxin. Am Heart J. 1984 Oct;108(4 Pt 2):1121–1127. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90592-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreifus L. S., Mazgalev T. "Atrial paralysis": does it explain the irregular ventricular rate during atrial fibrillation? J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Mar;11(3):546–547. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)91529-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogelman A. M., La Mont J. T., Finkelstein S., Rado E., Pearce M. L. Fallibility of plasma-digoxin in differentiating toxic from non-toxic patients. Lancet. 1971 Oct 2;2(7727):727–729. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)92100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. R., Aronson J. K., Grahame-Smith D. G., Carver J. G. The acute changes seen in cardiac glycoside receptor sites, 86rubidium uptake and intracellular sodium concentrations in the erythrocytes of patients during the early phases of digoxin therapy are not found during chronic therapy: pharmacological and therapeutic implications for chronic digoxin therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;8(2):135–142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb05811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S., Probst P., Selzer A., Cohn K. Inefficacy of "therapeutic" serum levels of digoxin in controlling the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 1975 May;35(5):651–655. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(75)90051-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Güllner H. G., Stinson E. B., Harrison D. C., Kalman S. M. Correlation of serum concentrations with heart concentrations of digoxin in human subjects. Circulation. 1974 Oct;50(4):653–655. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.50.4.653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkin H., Kleiner A., Saginer A., Almog S., Millman P., Tirosh M. Value of serum digoxin concentration measurement in the control of digoxin therapy in atrial fibrillation. Isr J Med Sci. 1979 Jun;15(6):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härtel G., Kyllönen K., Merikallio E., Ojala K., Manninen V., Reissell P. Human serum and myocardium digoxin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Feb;19(2):153–157. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976192153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jogestrand T. Digoxin concentration in right atrial myocardium, skeletal muscle and serum in man: influence of atrial rhythm. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Apr;17(4):243–250. doi: 10.1007/BF00625797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jogestrand T., Nordlander R. Serum digoxin determination in outpatients--need for standardization. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;15(1):55–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01463.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joreteg T., Jogestrand T. Physical exercise and binding of digoxin to skeletal muscle--effect of muscle activation frequency. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;27(5):567–570. doi: 10.1007/BF00556893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsh J. A., Sahakian A. V., Baerman J. M., Swiryn S. Ventricular response to atrial fibrillation: role of atrioventricular conduction pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Nov;12(5):1265–1272. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)92610-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein H. O., Kaplinsky E. Verapamil and digoxin: their respective effects on atrial fibrillation and their interaction. Am J Cardiol. 1982 Oct;50(4):894–902. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(82)91251-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGENDORF R., PICK A. VENTRICULAR RESPONSE IN ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. ROLE OF CONCEALED CONDUCTION IN THE AV JUNCTION. Circulation. 1965 Jul;32:69–75. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.32.1.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R., Klein H. O., Weiss E., David D., Sareli P., Levy A., Guerrero J., Di Segni E., Kaplinsky E. Superiority of oral verapamil therapy to digoxin in treatment of chronic atrial fibrillation. Chest. 1983 Mar;83(3):491–499. doi: 10.1378/chest.83.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Laing E., Moreland T. A., Service E., McDevitt D. G. A comparison of digoxin, diltiazem and their combination in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1988 Mar;9(3):279–283. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R., Lakhani M., Moreland T. A., McDevitt D. G. A comparison of verapamil and digoxin in the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 1987 Feb;8(2):148–153. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a062242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd B. L., Taylor R. R. Influence of myocardial mechanical activity and coronary blood flow on myocardial digoxin uptake. Cardiovasc Res. 1976 Jul;10(4):487–493. doi: 10.1093/cvr/10.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd B. L., Taylor R. R. The effect of heart rate on myocardial ouabain uptake and on the susceptibility to ouabain cardiotoxicity in the dog. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1978 Mar-Apr;5(2):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1978.tb00667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijler F. L., Fisch C. Does the atrioventricular node conduct? Br Heart J. 1989 Apr;61(4):309–315. doi: 10.1136/hrt.61.4.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijler F. L., Kroneman J., van der Tweel I., Herbschleb J. N., Heethaar R. M., Borst C. Nonrandom ventricular rhythm in horses with atrial fibrillation and its significance for patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1984 Aug;4(2):316–323. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(84)80220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. E., Madsen J., Kjaer K., Klitgaard N. A., Hvidt S. Effects of physical activity and immobilization on plasma digoxin concentration and renal digoxin clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Sep;34(3):303–308. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfors A. Digoxin dosage and ventricular rate at rest and exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation. Acta Med Scand. 1971 Oct;190(4):321–333. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1971.tb07437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth A., Harrison E., Mitani G., Cohen J., Rahimtoola S. H., Elkayam U. Efficacy and safety of medium- and high-dose diltiazem alone and in combination with digoxin for control of heart rate at rest and during exercise in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 1986 Feb;73(2):316–324. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.73.2.316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. W. Digitalis. Mechanisms of action and clinical use. N Engl J Med. 1988 Feb 11;318(6):358–365. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198802113180606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg J. S., Katz R. J., Bren G. B., Buff L. A., Varghese P. J. Efficacy of oral diltiazem to control ventricular response in chronic atrial fibrillation at rest and during exercise. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1987 Feb;9(2):405–411. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(87)80396-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallenstein S., Zucker C. L., Fleiss J. L. Some statistical methods useful in circulation research. Circ Res. 1980 Jul;47(1):1–9. doi: 10.1161/01.res.47.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittkampf F. H., de Jongste M. J., Lie H. I., Meijler F. L. Effect of right ventricular pacing on ventricular rhythm during atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988 Mar;11(3):539–545. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(88)91528-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


