Fig 1. CCX559 selectively inhibited in vitro binding of human PD-L1 to PD-1 and CD80, and enhanced TCR signaling in Jurkat cells.
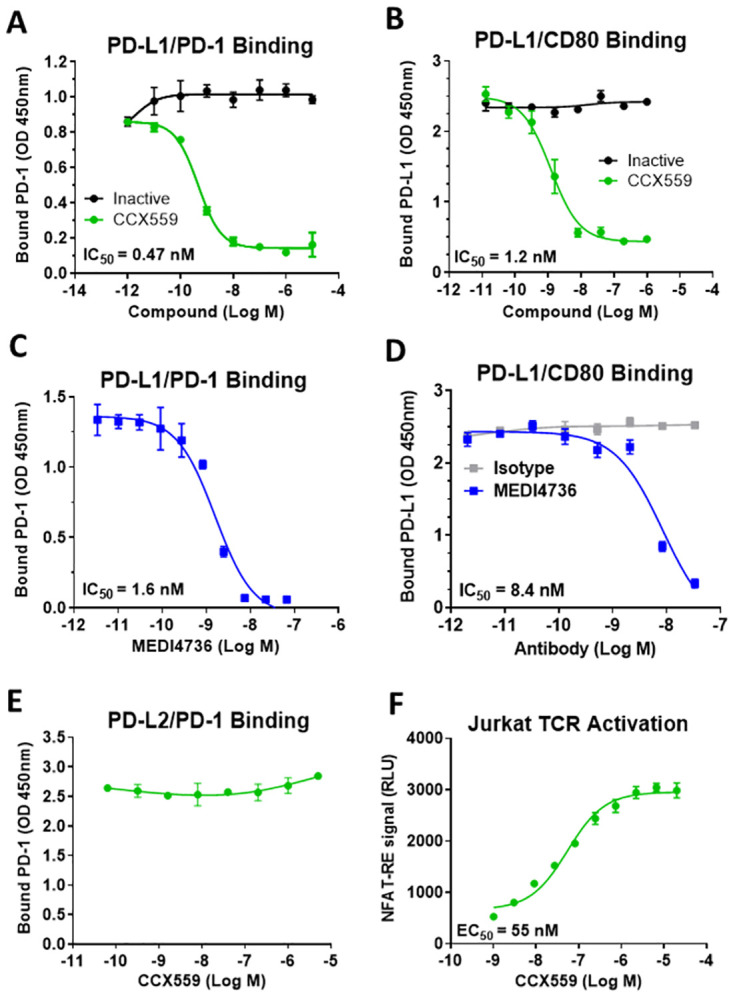
(A) Recombinant PD-1 binding to plate-bound PD-L1 was inhibited by CCX559 with an IC50 of 0.47 nM, as shown in a representative assay (green circles). An inactive compound with a similar structure to CCX559 had no effect on binding (black circles). (B) PD-L1 binding to plate-bound CD80 was inhibited by CCX559 (green circles) but not by the inactive compound (black circles). (C) The anti-PD-L1 antibody MEDI4736 inhibited PD-L1 binding to PD-1 in the same assay as in A. (D) CD80 binding was also inhibited by MEDI4736 (blue squares), but not by the isotype control (grey squares) in the same assay as B. (E) PD-1 binding to PD-L2 was not affected by up to 5 μM CCX559. (F) CCX559 enhanced TCR activation in a Jurkat cell-based NFAT reporter assay performed in 100% FBS to mimic physiological conditions. The graph is representative of all assays performed. EC50 and IC50 values were calculated with GraphPad Prism using 3-parameter nonlinear regression. The error bars represent ± one standard deviation (SD, n = 3 replicates).
