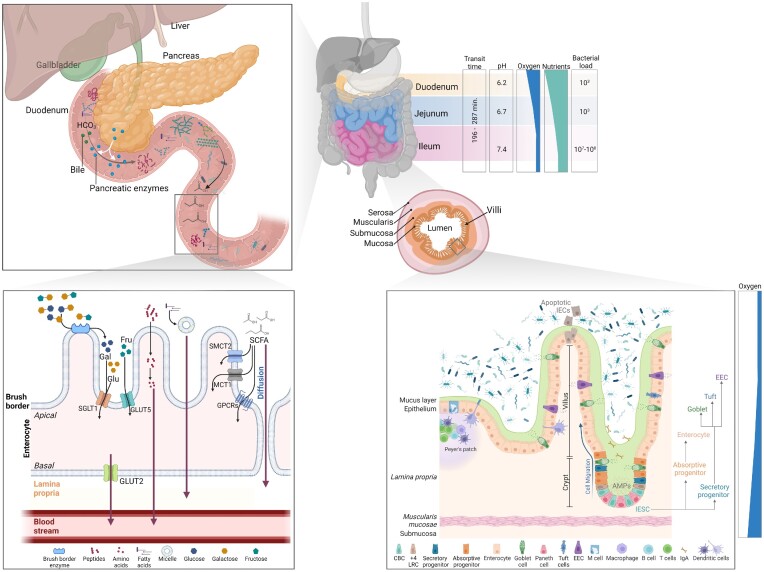
Figure 1.
Overview of small intestinal anatomy, histology, and key processes for food digestion and absorption. Physico-chemical parameters, and bacterial load (CFU/ml) are indicated for each segment of the small intestine. pH values are based on Ibekwe et al. (2008) in fasted patients. Cell types present on the small intestinal epithelium are represented. Key digestive processes taking place in the small intestine are summarized in the top left-hand panel and, below, the major transport pathway for nutrient absorption. IESC: intestinal epithelial stem cell; IECs: intestinal epithelial cells; CBC: crypt base columnar cell; +4 LRC: +4 label retaining cell; EEC: enteroendocrine cells; IgA: immunoglobulin A; AMPs: antimicrobial peptides; Gal: galactose; Glu: glucose; Fru: fructose; SCFA: short-chain fatty acids; and GPCRs: G-protein coupled receptors. Created with BioRender.com.