Abstract
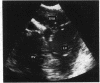
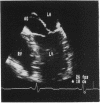
OBJECTIVE--To evaluate the clinical usefulness of transoesophageal echocardiography in the assessment of children with fixed left ventricular outflow tract stenosis. PATIENTS AND METHODS--Eight consecutive children, aged over 5 years, with fixed subaortic stenosis and one child with fixed subpulmonary left ventricular outflow tract stenosis were prospectively assessed by precordial and transoesophageal echocardiography. RESULTS--Transoesophageal images of the left ventricular outflow tract were much clearer than precordial images in all patients except one with a prosthetic mitral valve. Improved visualisation provided further information on the nature of the lesion (additional chordal attachment of the mitral valve in one, accessory atrioventricular valve tissue with aneurysm formation in one), on the extent of the lesion (circumferential in three), and on the very close relation of a ridge to the aortic valve leaflets in one. Transoesophageal Doppler did not provide any additional information on aortic regurgitation and was unreliable for gradient estimation across the left ventricular outflow tract. CONCLUSIONS--Transoesophageal imaging provides an excellent means of visualising lesions in the left ventricular outflow tract and can be useful in a few children and adolescents in whom precordial echocardiography does not provide adequate information. The technique can also be used intraoperatively to define the full extent of the obstructive lesion and to assess residual lesions after surgery.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Motro M., Schneeweiss A., Shem-Tov A., Vered Z., Hegesh J., Neufeld H. N., Rath S. Two-dimensional echocardiography in discrete subaortic stenosis. Am J Cardiol. 1984 Mar 15;53(7):896–898. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(84)90520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mügge A., Daniel W. G., Wolpers H. G., Klöpper J. W., Lichtlen P. R. Improved visualization of discrete subvalvular aortic stenosis by transesophageal color-coded Doppler echocardiography. Am Heart J. 1989 Feb;117(2):474–475. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(89)90795-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinger M. E., Kronzon I. Improved evaluation of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction by transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1989 May-Jun;2(3):191–194. doi: 10.1016/s0894-7317(89)80057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seward J. B., Khandheria B. K., Oh J. K., Abel M. D., Hughes R. W., Jr, Edwards W. D., Nichols B. A., Freeman W. K., Tajik A. J. Transesophageal echocardiography: technique, anatomic correlations, implementation, and clinical applications. Mayo Clin Proc. 1988 Jul;63(7):649–680. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)65529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreeram N., Sutherland G. R., Bogers J. J., Stümper O., Hess J., Bos E., Quaegebeur J. M. Subaortic obstruction: intraoperative echocardiography as an adjunct to operation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 Oct;50(4):579–585. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90193-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart J. R., Merrill W. H., Hammon J. W., Jr, Graham T. P., Jr, Bender H. W., Jr Reappraisal of localized resection for subvalvar aortic stenosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 Aug;50(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90733-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]