Figure 2.
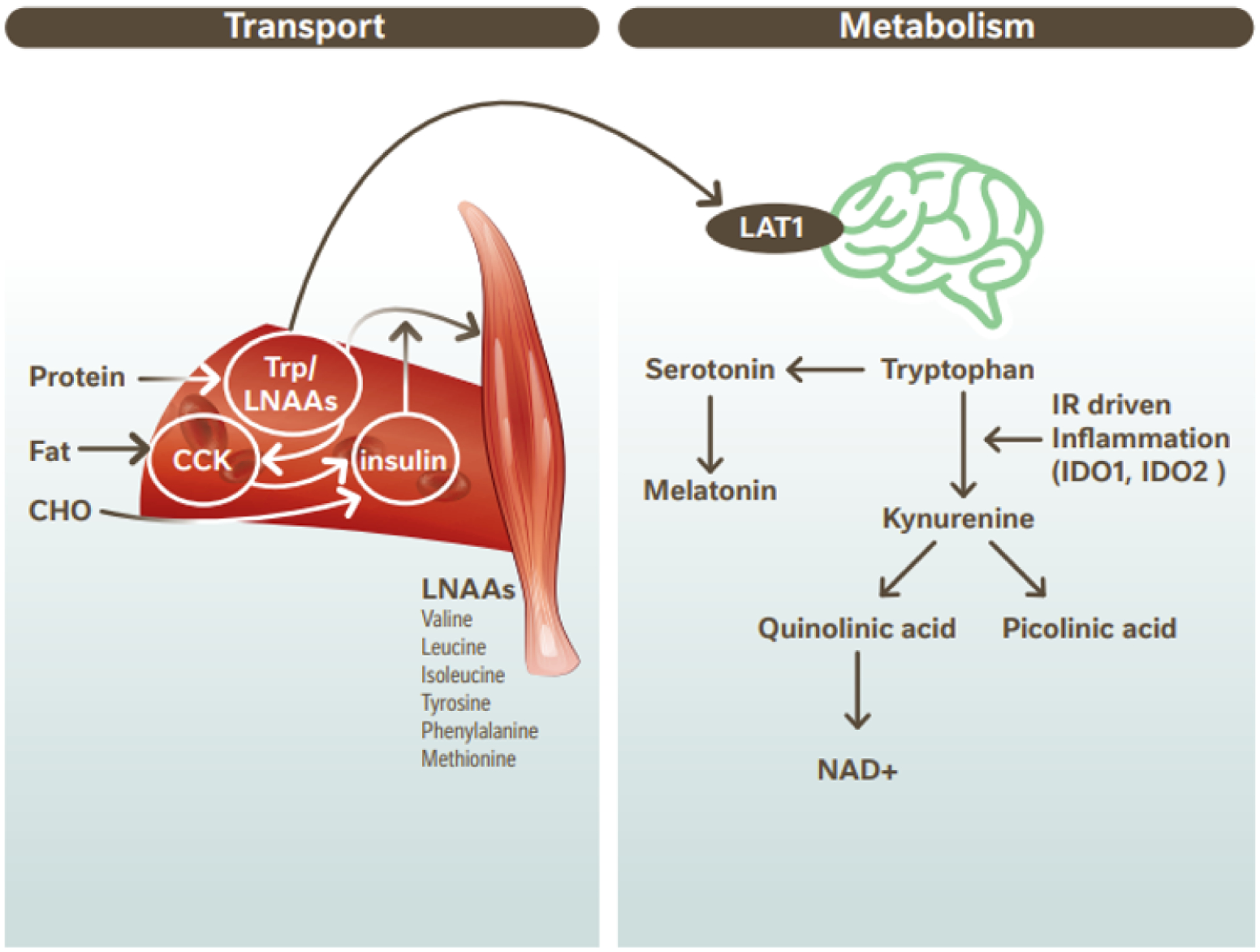
Transport and metabolism of dietary Trp in the CNS. Trp is derived from dietary protein along with other LNAAs. Transport of Trp/ LNAAs compete at Large Neutral Amino Acid Transporter (LAT1) sites. CHO ingestion leads to insulin secretion and dietary fat increases CCK which may also induce insulin secretion. Elevated insulin drives LNAA into muscle tissue excluding Trp. Trp transport into the brain is thus upregulated. In the brain Trp is metabolized to serotonin and melatonin or is metabolized via the kynurenine pathway. In individuals with obesity-induced inflammation leading to IR, the kynurenine pathway is upregulated. Diagram adapted from Cheon & Kim (67) CCK, cholecystokinin; CHO, carbohydrate; CNS, central nervous system; IDO, indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase; IR, insulin resistance; Trp; Tryptophan; LAT1, large neutral amino acid transporter 1; LNAA, large neutral amino acids.
