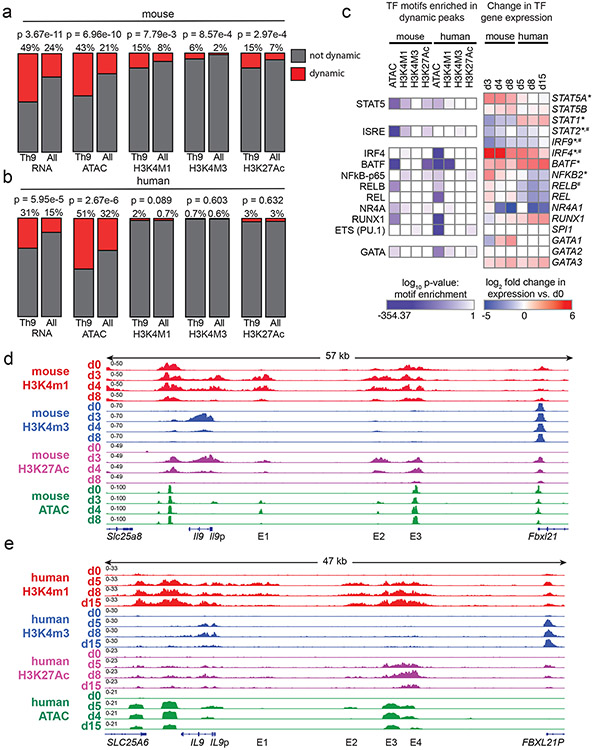
Figure 4. Prolonged resting of Th9 cells reduces accessibility of STAT5 binding sites and type 2 cytokine loci, including critical IL9 enhancers.
a,b. Bar graphs show enrichment (2-sided Fisher’s t-test) in murine (a) and human (b) Th9 cells of dynamically expressed genes, dynamic ATAC-seq (accessibility) peaks, dynamic H3K4Me1 (poised enhancer) peaks, dynamic H3K4Me3 (active promoter) peaks, and dynamic H3K27Ac (active enhancer) peaks in loci/genes mapping to the ‘allergic Th9” cassette vs. all coding gene loci. c. Heatmap (left) shows log (p-value, HOMER de novo motif discovery) for motif enrichment of transcription factors (TF) in human and murine dynamic peaks. All motifs with significant enrichment in at least 1 murine peak set and at least 1 human peak set are shown. Heatmap (right) shows log2 (average fold-change) in gene expression of TFs with motif enrichment in dynamic peaks. Values are shown for murine and human Th9 at various time points vs. naïve T cells. * transiently upregulated in murine Th9 (FC >2, FDR < 0.05, d3-d4 vs. d0-d8) # transiently upregulated in human Th9 (FC >2, FDR < 0.05, d5-d8 vs. d0-d15); d, e. Genome tracks show poised enhancer (H3K4Me1), active promoter (H3K4Me3), active enhancer (H3K27Ac) marks, and accessibility (ATAC) of the murine Il9 (d) and human IL9 (e) extended locus including the promoter (Il9p), downstream enhancer (DS) and upstream enhancers 1-4 (E1-E4), at different time points during Th9 differentiation and resting. All replicates are biologically independent samples.