Figure 6: WHIM CD8+ T cells undergo normal activation and differentiation in response to acute LCMV infection.
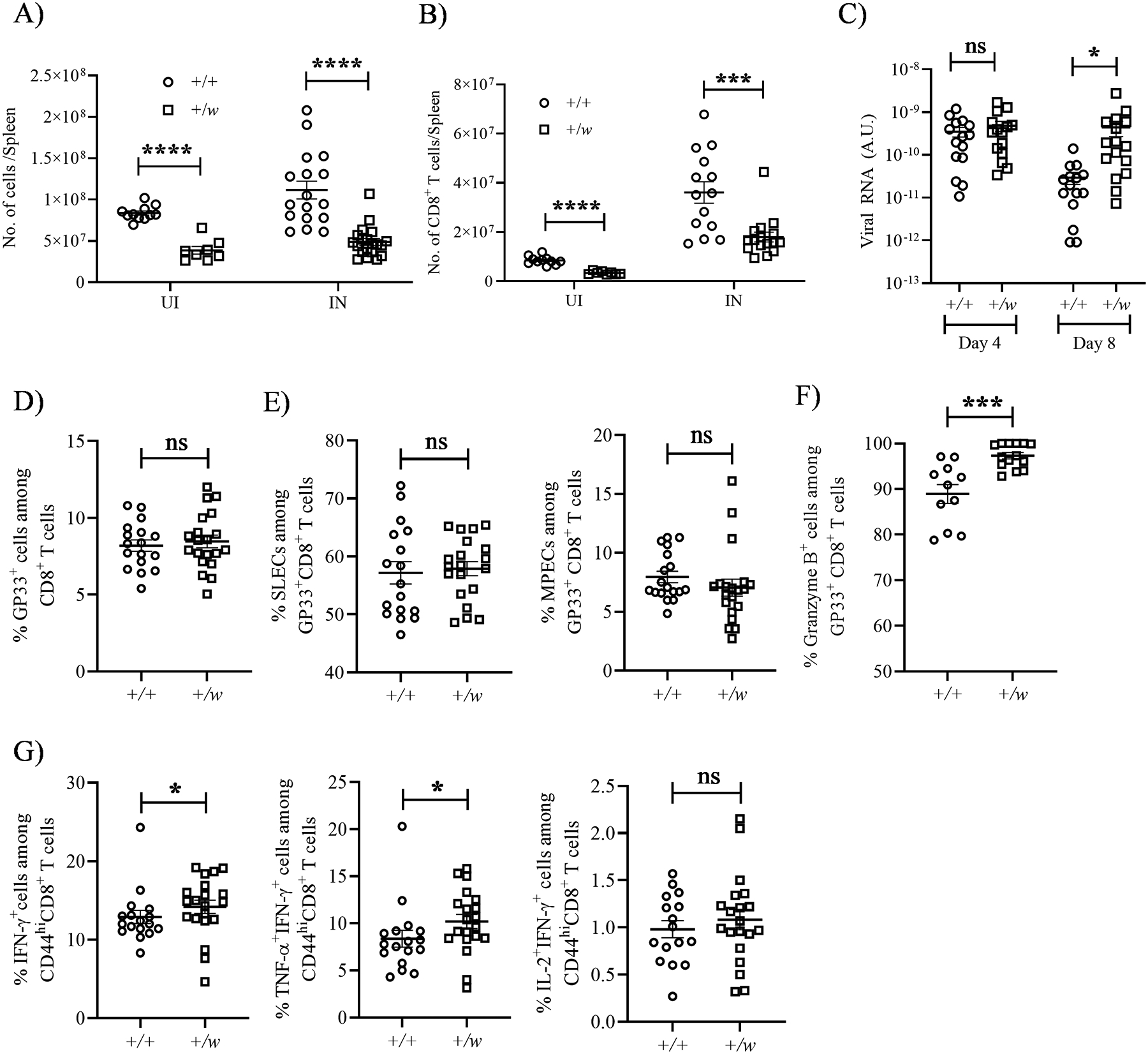
+/+ and +/w mice were infected i.p. with 2 × 105 plaque forming units/mouse of LCMV (Armstrong strain). On day 8 after infection, infected and uninfected mice were sacrificed, and their splenocytes were analyzed by FACS. (A and B) Total splenic cellularity and CD8+ T cell numbers. The Cxcr4 genotypes and infection status are indicated on the x-axes. +, wild type; w, WHIM; UI, uninfected; IN, infected. (C) Viral burden. The viral burdens in sera on days 4 and 8 post infection were quantified by RT-PCR for the conditions indicated on the x-axis. (D and E) Differentiation. (D) LCMV peptide GP33 tetramer-specific CD8+ T cells were gated to quantify the (E) SLEC (short lived effector cells, KLRG1hiCD127/IL-7Rαlo) and MPEC (memory precursor effector cells, KLRG1loCD127/IL-7Rαhi) subsets. (F and G) Activation. The proportions of LCMV-specific CD8+ T cells expressing the factors shown at the top of each panel were quantitated by intracellular staining. (G) Cytokines were measured after in vitro stimulation of GP33+CD44+ splenocytes. The Cxcr4 genotypes of the mouse groups are shown as insets in A and B and on the x-axes for C-G. +, wild type; w, WHIM allele. Data are summarized as the mean ± SEM of at least 8 mice per genotype from 3–4 independent experiments. ns: not significant, *, p< 0.05, ***, p< 0.001 and ****, p< 0.0001 as determined by the two-tailed unpaired t test for A-D, E (left panel), F and G (right most panel) and Mann Whitney test for E (right panel) and G (first two panels).
