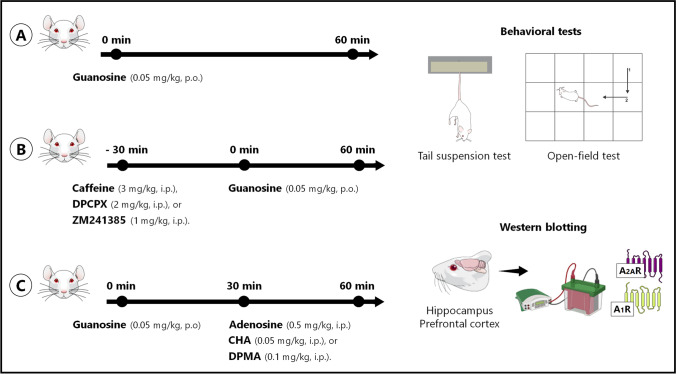
Fig. 1.
Schedule of experimental approaches, pharmacological treatments, behavioral tests, and Western blotting analysis. In the first experimental approach, female Swiss mice were administered orally (p.o.) with vehicle or guanosine (0.05 mg/kg, p.o.), and 60 min after the treatments, they were subjected to the tail suspension test and open-field test (10 min apart). After the behavioral tests, mice were immediately euthanized by decapitation and the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex were dissected to measure the immunocontent of adenosine A1R and A2AR by Western blotting (A). In the second experimental approach, mice were pretreated with vehicle, caffeine (3 mg/kg, i.p.), DPCPX (2 mg/kg, i.p.), or ZM241385 (1 mg/kg, i.p.) and 30 min after the treatments, they received the administration of vehicle or guanosine (0.05 mg/kg, p.o.). Following 60 min of the treatments, mice were subjected to the tail suspension test and open-field test (B). In the third experimental approach, mice were treated with vehicle or guanosine (0.05 mg/kg, p.o.), and following 30 min, they received the administration of adenosine (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.), CHA (0.05 mg/kg, i.p.), or DPMA (0.1 mg/kg, i.p.). After 30 min of the treatments, mice were subjected to the tail suspension test and open-field test (C). Figure designed using images from Mind the Graph