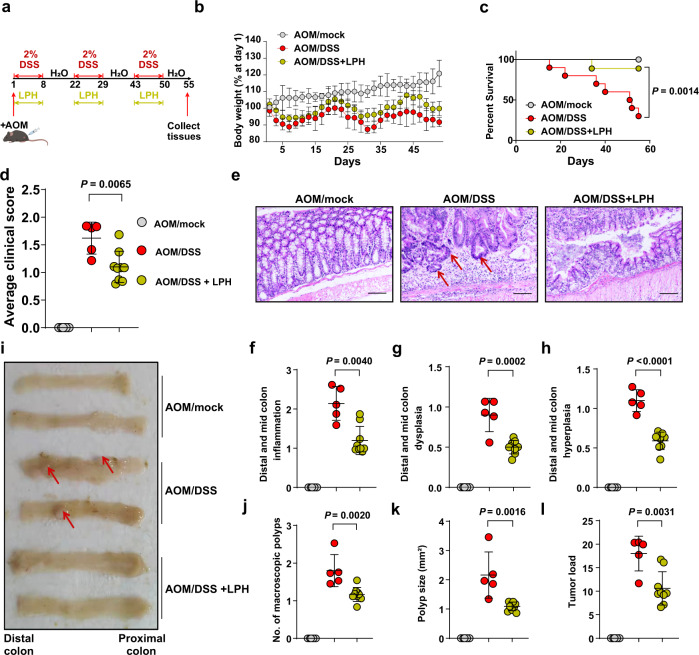
Fig. 6. LPH can protect mice against colitis-associated colon cancer.
a Schematic of experimental design for the AOM/DSS induced colon cancer model. AOM/mock mice were intraperitoneally injected with AOM (10 mg/kg body weight) following drinking water. BSA or LPH-containing beads (5 mg/kg body weight) were orally administered during the three cycles of DSS treatment. (AOM/mock, n = 8; AOM/DSS n = 12; AOM/DSS + LPH, n = 10). Images were created using BioRender.com. b, c Loss of body weight (b) and survival rates (c) of mice treated with AOM/mock, AOM/DSS or AOM/DSS + LPH. d Average clinical scores of mice treat with AOM/mock (n = 8), AOM/DSS (n = 5) or AOM/DSS + LPH (n = 9). e–h Representative H&E staining of colonic tissue, scale bar, 200 μm (e); semiquantitative score of colonic inflammation (f); dysplasia (g) and hyperplasia (h) in mice treat with AOM/mock (n = 8), AOM/DSS (n = 5) or AOM/DSS + LPH (n = 9). i-l Representative images of colons (i); macroscopic polyp counts (j); average polyp size (k) and tumor load (l) in mice treat with AOM/mock (n = 8), AOM/DSS (n = 5) or AOM/DSS + LPH (n = 9). AOM: azoxymethane; BSA: bovine serum albumin. Data are representative of 2 independent experiments and presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analyses were performed using Log-rank test (c), two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (d, f, g, h, j–l). Source data are provided as a Source data file.