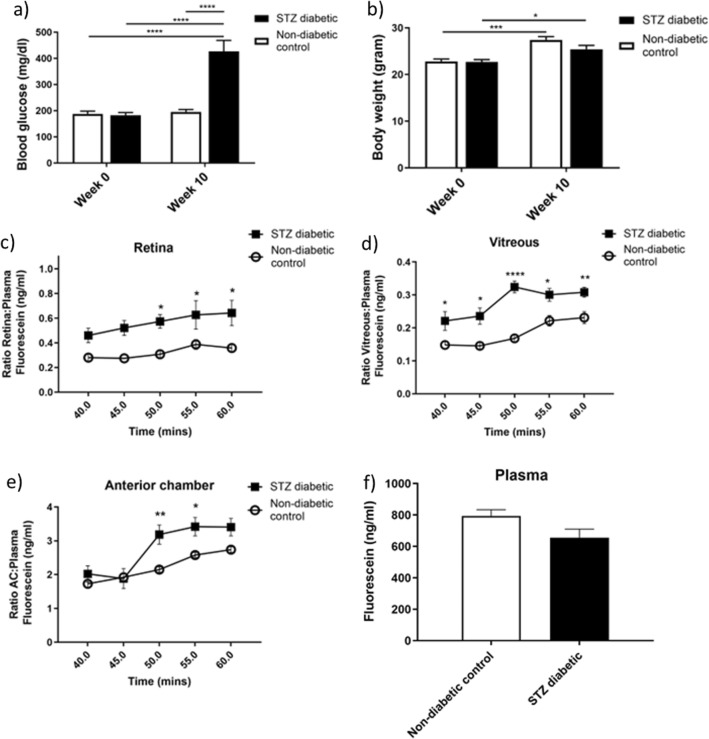
Figure 4.
Quantification of permeability in the streptozotocin (STZ) diabetic mouse model using fluorophotometry. Mice that had been induced with STZ to be diabetic 10 weeks previously were used in this experiment, and compared with age-matched non-diabetic control animals. (a) Blood glucose levels were significantly elevated in STZ diabetic mice, 10 weeks following diabetes induction, whereas (b) body weight was not significantly different from non-diabetic control mice. Levels of fluorescein in (c) the retina, (d) the vitreous and (e) the anterior chamber were all significantly increased in STZ mice at various time points from 40 to 60 min post-injection of 50 mg/kg subcutaneous fluorescein, compared with non-diabetic controls. Data shown in (c–e) are corrected to plasma levels of fluorescein. (f) Plasma levels of fluorescein were not significantly different between STZ diabetic and non-diabetic control mice treatment groups. N = 6–16 eyes per time point. Blood glucose and body weight assessed statistically by Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures, followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Ocular compartment leakage assessed statistically by Two-way ANOVA with repeated measures, followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001. Data are given as means ± SEM.