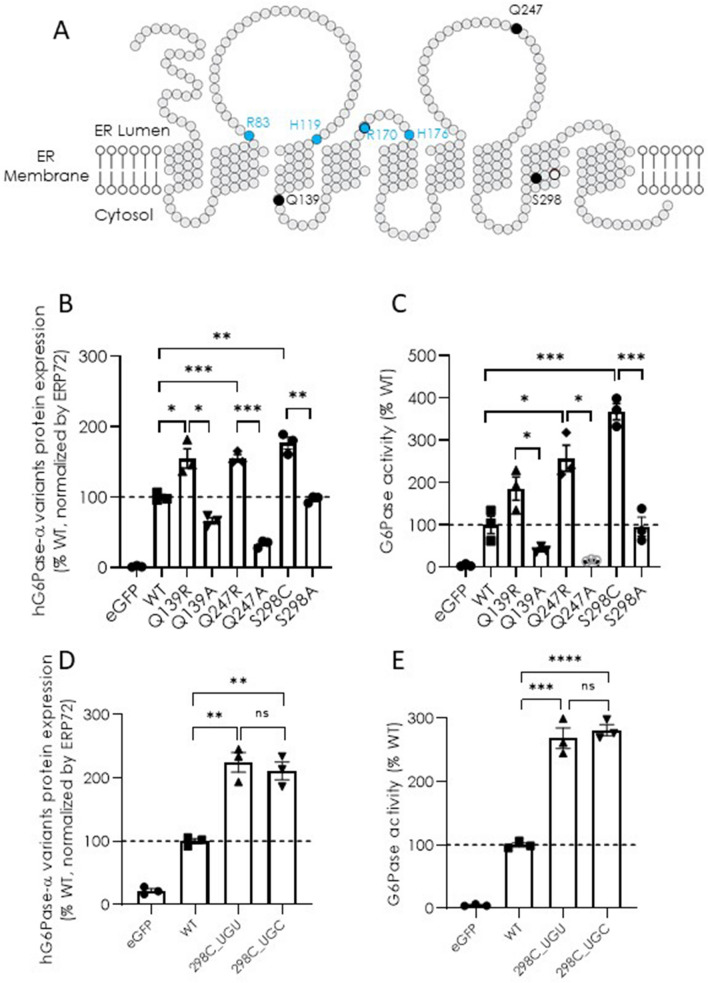
Fig. 1.
Protein expression and G6Pase enzymatic activity of hG6Pase-α variants directed by hG6PC mRNA constructs. A Topological analysis of hG6Pase-α shows a nine-transmembrane spanning ER enzyme. Black dots: locations of Q139, Q247, and S298 for targeted substitutions. Blue dots: residues directly involved in enzymatic activity. B and C protein expression (B) and G6Pase enzymatic activity (C) of hG6Pase-α variants encoded by hG6PC mRNA constructs encoding wild-type protein (WT) or protein variants containing a point mutation as indicated. D and E protein expression (D) and G6Pase enzymatic activity (E) of WT and the S298C hG6Pase-α variants encoded by two different codons at the mutated site. The mRNA constructs were transfected into HeLa cells and examined for protein expression and G6Pase activity in cell lysates at 48-h post-transfection, as described under “Materials and methods”. For protein expression analysis, the quantified signals from the hG6Pase-α variants were also normalized by Erp72, a house-keeping ER marker protein. Data were shown as percentage of wild-type (WT) group and presented as mean ± SEM of n = 3 samples from independent transfections. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.00, ****p < 0.0001. ns non-significant