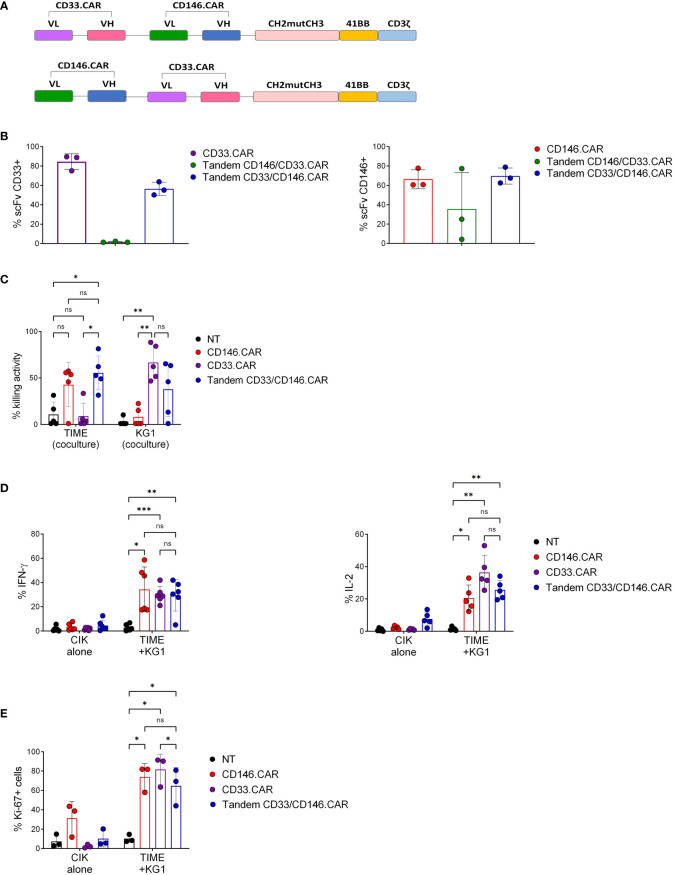
Figure 2.
Developing second-generation Tandem CD33/CD146.CAR CIK cells able to recognize simultaneously CD33+ KG-1 and CD146+ TIME cells, and to display full CAR in vitro effector functions. (A) Schematic diagram of Tandem CAR molecules’ structure, including CD33 and CD146 scFvs in the different position, CH2mutCH3 (Long) as spacer sequence, 4-1BB as co-stimulatory domain and CD3ζ signaling domain. (B) Percentage of expression of CD33 and CD146 scFv by CIK cells at day 21 of culture, determined by FACS analysis(n=3). (C) Short-term cytotoxicity of untransduced (NT), single CD33- and CD146- CAR CIK cells and Tandem CD33/CD146.CAR CIK cells co-cultured with CD146+TIME and CD33+ KG-1 cells at 5:1 E:T ratio (n=3). (D) Cytokines production (IFN-γ and IL-2) by NT, single CD33- and CD146- CAR CIK cells and Tandem CD33/CD146.CAR CIK cells when engaged with TIME and KG-1 cells. IFN-γ and IL-2 were detected by intracellular staining after 5-hours co-culture at 1:3 E:T ratio (n=3). (E) Proliferation determined by intracellular Ki-67 staining of NT, single CD33- and CD146- CAR CIK cells and Tandem CD33/CD146.CAR CIK cells after co-culture with TIME cells and KG-1 for 72 hours at 1:1 E:T ratio (n=3). (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, Two-way ANOVA analysis with Benjamini and Hochberg’s multiple comparisons test). NS, not significant.