Figure 1. Characterization of biallelic intragenic SVs (family 1) and a homozygous SNV (family 2) in FGF12.
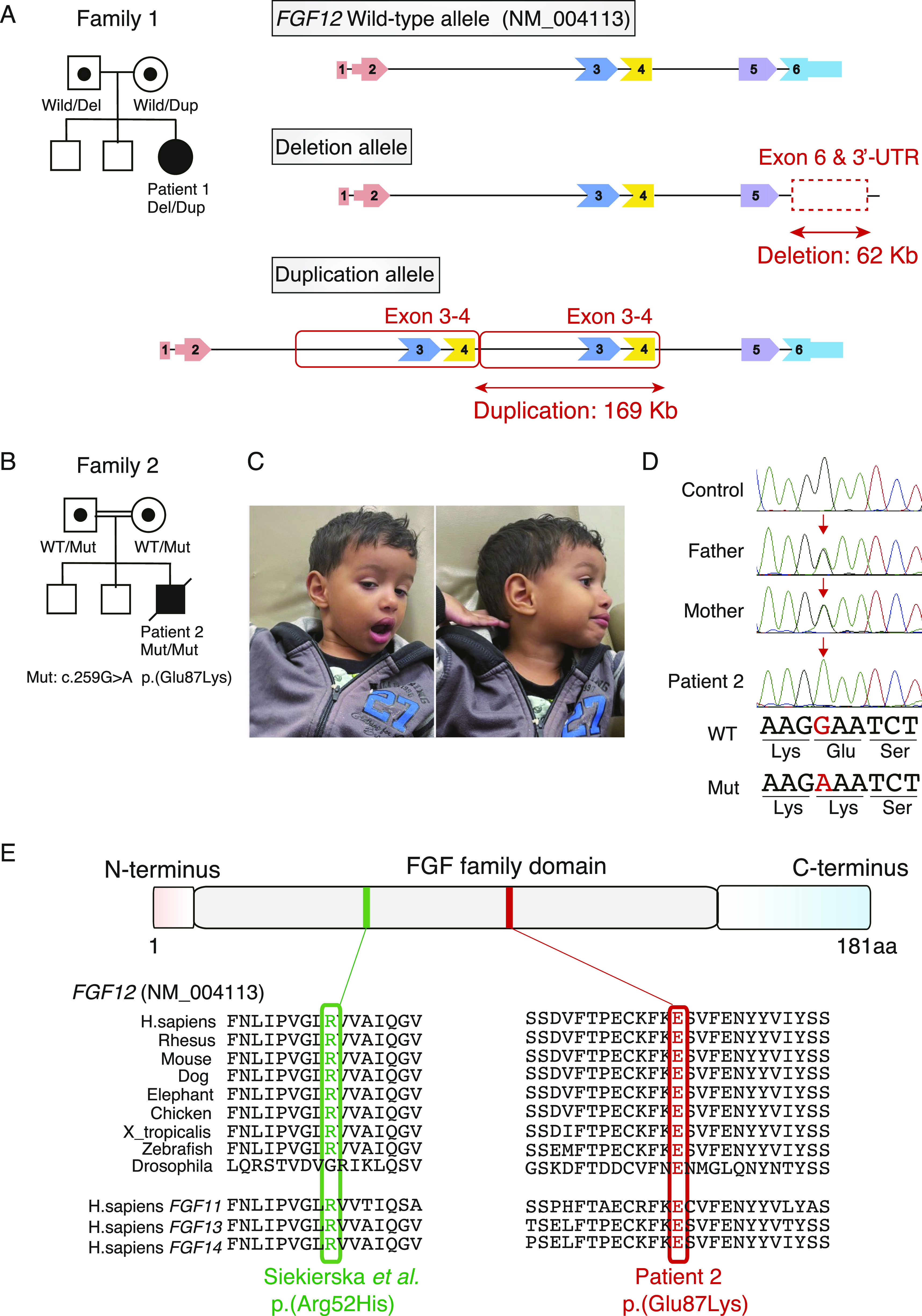
(A) The pedigree and biallelic intragenic SVs in FGF12 of family 1. Wild-type and aberrant alleles harboring intragenic deletion and duplication in patient 1 and her parents. FGF12 transcripts consist of two main isoforms, isoform-A (NM_021032) and isoform-B (NM_004113), containing five and six exons, respectively, that differ in the N-terminal sequences. In this study, all FGF12 variants are described based on the reference sequence NM_004113, because isoform-B is most abundant in the human brain (GTEx portal) and is also selected as a representative transcript by the Matched Annotation from NCBI and EMBL-EBI (MANE) project. Wild, FGF12 wild-type allele; Del, FGF12 intragenic deletion allele; Dup, FGF12 intragenic tandem duplication allele. (B) The pedigree in family 2. WT, wild-type allele; Mut, variant allele harboring c.259G>A p.(Glu87Lys). (C) Facial photographs of patient 2 at the age of 4 yr, showing a broad forehead and pointed chin. (D) Electropherograms of the homozygous missense variant in FGF12 of family 2. Patient 2 has a homozygous missense variant, c.259G>A p.(Glu87Lys), inherited from each of his parents. The corresponding nucleotides and amino acid residues are shown under the electropherograms. WT, wild-type allele; Mut, variant allele harboring c.259G>A p.(Glu87Lys); Red arrows, location of the variant. (E) Schematic presentation of the FGF12 protein corresponding to isoform-B (NM_004113) with functional domains showing a homozygous SNV in patient 2 together with a recurrent gain-of-function variant. Red and green variants represent p.Glu87Lys in patient 2 and a recurrent gain-of-function variant, p.Arg52His, respectively. Both pathogenic variants occur at amino acids that are evolutionarily well conserved among species (Vertebrate Multiz Alignment & Conservation [100 Species] and Multiz Alignment & Conservation [124 insects] on UCSC genome browser). aa, amino acids.
