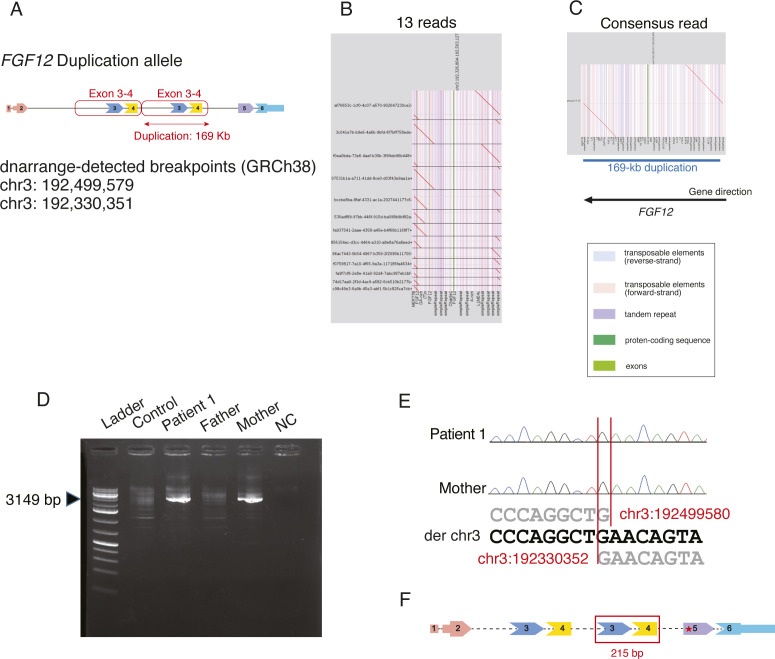
Figure S3. Characterization of a tandem duplication allele in FGF12 of patient 1.
(A) Schematic presentation of a tandem duplication allele in patient 1. The positions of dnarrange-detected breakpoints in chromosome 3 were 192,499,579 and 192,330,351. (B) Dot plots of 13 reads derived from the tandem duplication allele. (C) Dot-plot picture of the consensus sequence made by lamassemble. The red line shows the alignment between the reference sequence and chr3:192,326,971–192,502,959 with a 169-kb intragenic-tandem duplication involving exons 3 and 4. The vertical stripes depict annotations in the reference genome with different colors: transposable elements (blue, reverse strand; pink, forward strand), tandem repeats (purple), protein-coding sequences (dark green), and exons (green). There is a 169-kb duplication at the breakpoints, and the blue line shows the extent of the duplication in the genome. The direction of the black arrow indicates the direction of the gene. (D) Duplication breakpoint PCR in the patient and her parents. Breakpoint PCR of the patient and her parents confirmed that the FGF12 duplication was derived from the mother. The PCR product was 3,149 bp in size. Control, an unrelated healthy control; NC, negative control (no DNA); Arrowhead, breakpoint PCR product containing the tandem duplication. (E) Electropherogram of tandem duplication breakpoints. dnarrange-predicted breakpoints made from lamassemble were nearly identical (only 1 base different to the Sanger sequencing results). (F) The duplicated coding segment (exons 3 and 4) is 215 bp in length. The position of premature termination codons created by the duplication is shown by a red asterisk in exon 5.