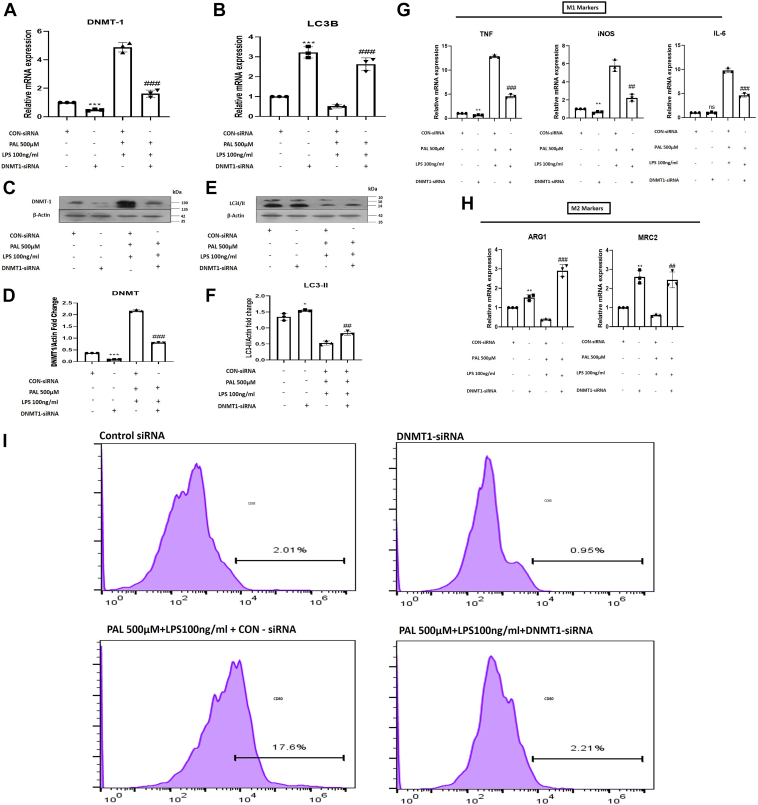
Figure 3.
DNMT1 silencing restores autophagy and macrophage polarization in RAW 264.7 macrophages.A, mRNA expression of DNMT1 in control-siRNA, DNMT1-siRNA, palmitate (500 μM)+LPS (100 ng/ml)+Control-siRNA, and palmitate (500 μM)+LPS (100 ng/ml)+DNMT1-siRNA-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. B, mRNA expression of LC3B in Control-siRNA, DNMT1-siRNA, palmitate+LPS+Control-siRNA, and palmitate (500 μM)+LPS (100 ng/ml)+DNMT1-siRNA-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. C, immunoblotting of DNMT1 in different groups indicated in the figure. D, bar graphs represent the densitometric ratio of DNMT1 to the corresponding β-actin. E, immunoblotting of LC3-II in different groups indicated in the figure. F, bar graphs represent the densitometric ratio of LC3-II to the corresponding β-actin. G, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of M1 markers (iNOS, TNF, and IL6) in different groups as indicated in the figure. H, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of M2 markers (ARG1 and MRC2) in different groups as indicated in the figure. I, flow cytometric analysis showed higher percentage of CD86+ (M1 macrophage marker) RAW 264.7 cells in palmitate+LPS+Control-siRNA-treated cells and decreased in palmitate (500 μM)+LPS (100 ng/ml) +DNMT1-siRNA-treated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Data are represented as mean ±SD, ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus Control-siRNA group; ##p < 0.01, and ###p < 0.001 versus Palmitate and LPS-treated group. Error bars (wherever applicable in the figure) represent standard deviations from 3 to 4 independent experiments.