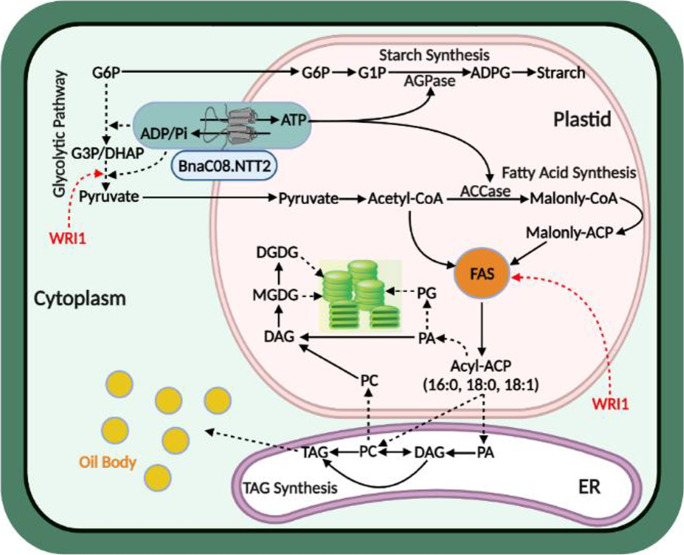
Fig. 7.
Proposed model depicting the functions of BnaNTT2 in cell metabolism. BnaNTT2 transports cytosolic ATP into plastid and exchanges ADP into cytoplasm. Overexpression of BnaC08.NTT2 promotes the transportation of more ATP into plastid and enhances starch and fatty acid synthesis. Enhanced metabolism in plastid promotes the glycolysis in cytoplasm. Meanwhile, WRI1 is a key transcription factor for fatty acid synthesis, playing a “push” role in fatty acid de novo synthesis. Loss function of BnaNTT2 decreases the transportation of ATP into plastid, leading to decreased fatty acid and chloroplast membrane lipid biosynthesis, which could result in abnormal thylakoid structure. AGPase, ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase; ACCase, acetyl-CoA carboxylase