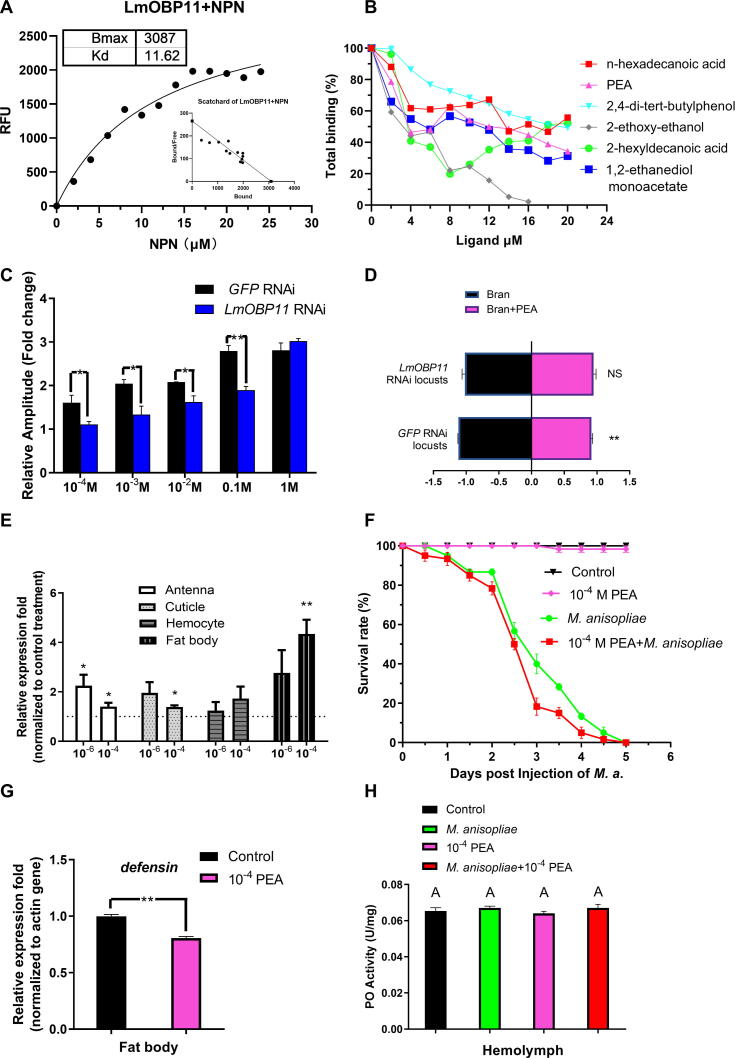
Fig. 3.
LmOBP11 binds to phenylethyl alcohol (PEA), and LmOBP11 knockdown results in loss of PEA avoidance behavior. (A) OBP binding to N-phenyl 1-napthylamine (1-NPN) and (B) binding affinities to volatile produced by M. anisopliae, namely phenylethyl alcohol, and another five volatiles, n-hexadecanoic acid, 2,4-di-tert-butylphenol, 2-ethoxy-ethanol, 2-hexyldecanoic acid and 1,2-ethanediol monoacetate, (C) Electroantennography of average antennal output in response to PEA, (D) aversion behavior of LmOBP11 dsRNA treated locusts to phenylethyl alcohol. (E) Relative expression analysis of LmOBP11 under various concentrations of PEA (mol/L). (F) Survival rates of locusts in response to PEA and M. anisopliae separately and collectively. (G) Expression of defensin in the fat body, and (H) PO activity in the hemolymph following treatment with 10−4 mol/L PEA and fungus infection. The Student's t-test was used to compare the means between treatment pairs, assuming they have equal variances. Asterisks indicate the level of statistical significance; *p < 0.05, *p < 0.01. Means followed by the same letter are not significantly different at p < 0.05 according to one-way ANOVA with the Post Hoc analysis of Bonferroni (equal variance).