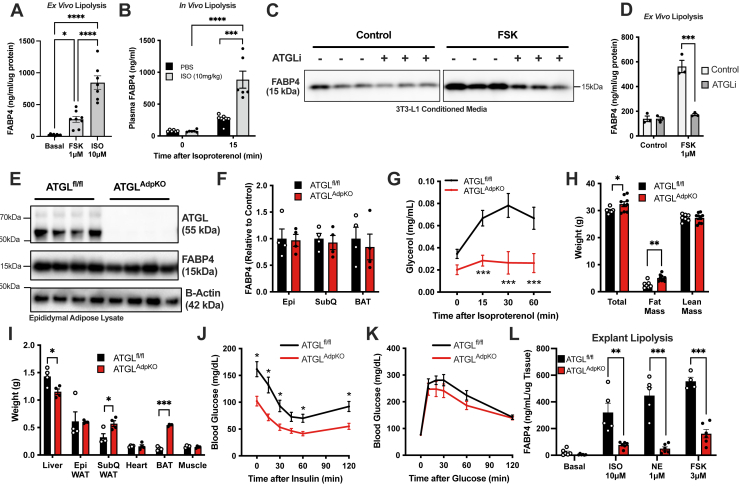
Fig. 1.
FABP4 secretion is dependent on lipolysis in vitro. A: FABP4 secretion from wild-type epididymal adipose tissue explants under unstimulated (basal) conditions or induction of lipolysis by FSK (1 μM) or ISO (10 μM) (N = 7–8/condition; one-way ANOVA). B: Plasma FABP4 in wild-type mice following injection of PBS or ISO (10 mg/kg) (N = 6/group; two-way ANOVA). FABP4 in conditioned media from (C) 3T3-L1 adipocytes (Western blot; FSK 10 μM) and (D) epididymal adipose tissue explants (ELISA quantification) following 2 h pretreatment with atglistatin (ATGLi; 10 μM) (N = 3/group; two-way ANOVA). E: Western blot of epididymal adipose tissue confirming ATGL deletion in ATGLAdpKO (N = 4/group). F: Quantification of FABP4 in adipose depots from ATGLfl/fl and ATGLAdpKO mice (N = 4/group; Student’s t-test). G: Plasma glycerol following induction of lipolysis in vivo (N = 14–16/group; two-way ANOVA). H: Body compo as determined by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) (N = 7–9/group; Student’s t-test). I: Weight of liver, epididymal (Epi) adipose tissue, subcutaneous (SubQ) adipose tissue, heart, brown adipose tissue (BAT), and gastrocnemius muscle (N = 4/group; Student’s t-test). Glucose excursion curves in (J) TT and (K) intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (ipGTT) (N = 9–10/group; two-way ANOVA). L: FABP4 secretion from epididymal adipose tissue explants under unstimulated (basal) conditions or induction of lipolysis by ISO (10 μM), NE (1 μM) or FSK (3 μM) (N = 4–6/condition; Student’s t-test). All mouse experiments performed in 8- to 10-week-old male mice. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.