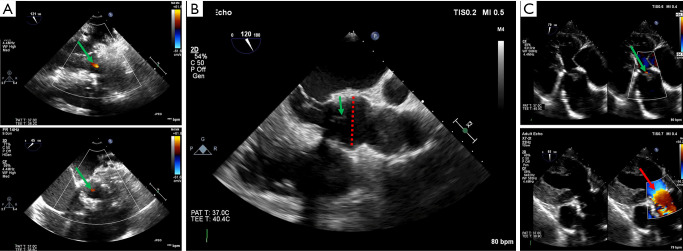
Figure 10.
Post-repair assessment. (A) Before aortic cross-clamp release, the effectiveness of the repair can be estimated by administering a terminal dose of blood cardioplegia into either the aortic root or tube graft. The root pressurization will oppose the cusps against each other. The non-pulsatile flow keeps the valve closed and helps to localize the origin and orientation of a residual jet (green arrow). (B) When the aortic annulus is functionally restored, the level of cusp coaptation should be above the aortic annulus. This means that the lower level of the coaptation should be higher than the ventriculo-arterial junction and its highest level (green arrow) should approach the mid-height of the sinuses of Valsalva (red dotted line). (C) The deep transgastric view is the best adapted to assess residual aortic regurgitation, because it avoids acoustic shadowing coming from the graft. It allows for detection of very mild regurgitation (green arrow), with a perfect alignment to calculate the transvalvular gradient and to assess the expected laminar trans-aortic flow (red arrow).