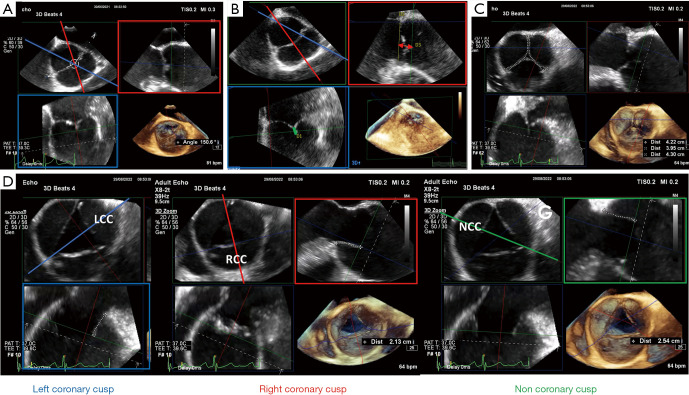
Figure 8.
Specific measurements of leaflet geometry. (A) The commissural orientation starting point is the center of the coaptation in diastole, formed by the crossing of two long-axis planes (red and blue plane). Then, the short-axis view is moved up to the edge of the functional commissures. The angle is measured on the non-fused cusp side, from the center of the coaptation to the higher point of the functional commissures. (B) The eH (red arrow) is measured from the annular plane to the tip of the cusp. The long-axis plane must be perpendicularly aligned (red line) to the entire body of the cusp on the short-axis plane. The cH (green line) is measured perpendicularly to the coaptation line. Thus, the cH plane differs from the eH plane by a few degrees (blue line). The cH calculation follows the entire visible coaptation. (C) The free margin lengths are measured in diastole on a short-axis plane reconstructed with the multiplanar reconstruction module and by using a curvilinear tool. (D) The gH can be measured for each cusp in systole. A plane is perpendicularly aligned to the free margin. The gH is measured on the corresponding orthogonal view (blue, LCC; red, RCC; green, NCC). eH, effective height; cH, coaptation height; gH, geometric height; LCC, left coronary cusp; RCC, right coronary cusp; NCC, non-coronary cusp.