Figure 2: hPSC-derived Schwann cells are transcriptionally similar to primary Schwann cells.
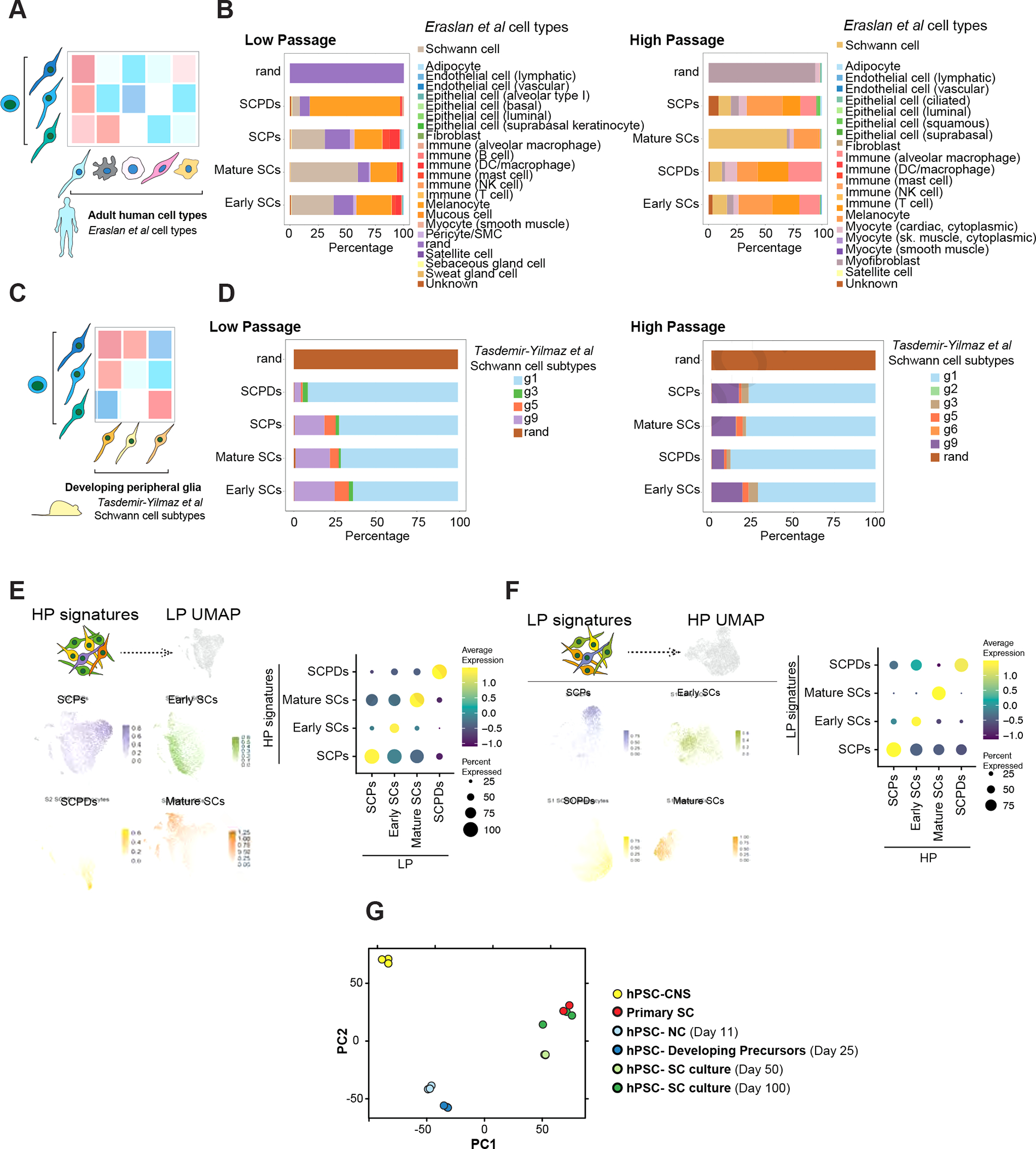
A) Schematic of comparing SCs with primary human adult cell types.
B) SingleCellNet26 classification of LP (left) and HP (right) SC clusters using the human cell atlas dataset27 as a reference.
C) Schematic of comparing SCs with primary mouse developing peripheral glia.
D) SingleCellNet26 classification of HP (left) and HP (right) SC clusters using a single cell transcriptomics mouse peripheral glia25 dataset as reference.
E, F) Module scoring of top 100 HP SC type specific differentially expressed (DE) marker genes in LP SC types (left). Feature (left) and dot plot (right) visualizations are depicted. Panel E shows the HP dataset module scored in LP dataset and panel F shows the other way comparison.
G) Principal component analysis (PCA) of NC cells, developing precursors, human primary SCs, and hPSC-derived SC cultures at D50 and D100 of differentiation in comparison with central nervous system (CNS) precursors.
